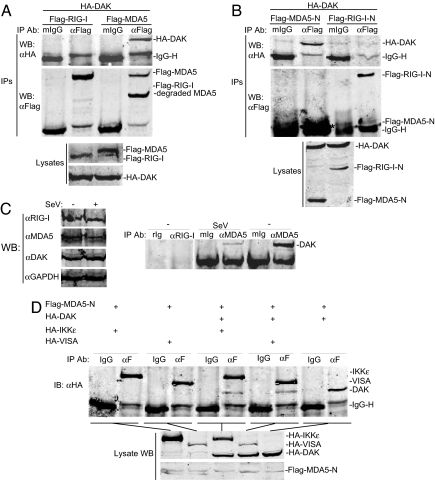
Fig. 1.
Identification of DAK as an MDA5-associated protein. (A) DAK interacts with MDA5 but not RIG-I in mammalian overexpression system. The 293 cells (2 × 106) were cotransfected with the indicated plasmids (5 μg each), and cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag antibody (αFlag) or control mouse IgG (mIgG). The immunoprecipitates were analyzed by Western blots with anti-HA (Top) or anti-Flag (Middle) antibody. Expression of the transfected proteins was analyzed by Western blots with anti-HA and anti-Flag antibodies (Bottom). (B) DAK interacts with N-terminal domain of MDA5. The experiments were similarly performed as in A. The asterisk (Middle) indicates the band of Flag-MDA5-N, which is close to the IgG light-chain band. (C) Endogenous association of DAK with MDA5. The 293 cells (1 × 108) were infected with SeV or left uninfected for 4 h. Cell lysate was immunoprecipitated with mouse anti-MDA5 or rabbit anti-RIG-I antiserum or control IgG. The immunoprecipitates were analyzed by Western blots with anti-DAK antibody (Right). The expression levels of the endogenous proteins were analyzed by Western blots with anti-MDA5, anti-DAK, and anti-RIG-I antibodies (Left). Each lane was loaded with whole-cell lysate from 5 × 106 cells. (D) Interactions between MDA5-N and DAK, IKKε and VISA. The 293 cells (2 × 106) were cotransfected with the indicated plasmids (5 μg of each). Coimmunoprecipitation and Western blot analysis were performed as in A. WB, Western blot; IP, immunoprecipitation; IB, immunoblot.