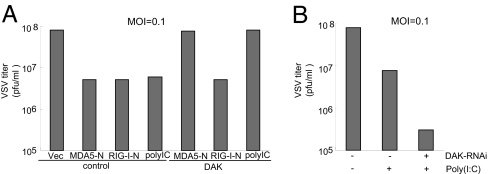
Fig. 5.
Effects of DAK and DAK RNAi on MDA5-mediated antiviral response. (A) DAK inhibits MDA5-mediated antiviral response. The 293 cells (2 × 105) were transfected with the indicated expression plasmids (1 μg of each). Twenty-four hours after transfection, cells were infected with VSV [multiplicity of infection (MOI) = 0.1], and supernatants were harvested at 12 h after infection. Supernatants were analyzed for VSV production by using standard plaque assays. Plaques were counted, and titers were calculated as plaque-forming units per milliliter. (B) DAK RNAi potentiates cytoplasmic poly(I:C)-triggered antiviral response. The 293 cells (2 × 105) were transfected with a control or DAK RNAi plasmid (1 μg of each). Thirty-six hours after transfection, cells were further transfected with poly(I:C) (20 μg) or buffer. Twelve hours later, cells were infected with VSV (MOI = 0.1), and supernatants were harvested at 12 h after infection for plaque assays.