Figure 1.
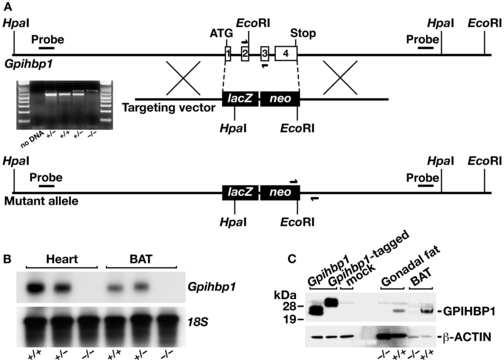
Generation of Gpihbp1 knockout mice. (A) Sequence-replacement gene-targeting strategy for inactivating Gpihbp1. Locations of the 5′ and 3′ probes (bars) for Southern blot analysis and PCR primers (arrows) for genotyping are shown. An ethidium-bromide stained agarose gel illustrates a PCR strategy for genotyping Gpihbp1+/+, Gpihbp1+/−, and Gpihbp1−/− mice. A description of the PCR genotyping strategy is contained in the Experimental Procedures. (B) A northern blot, probed with a Gpihbp1 cDNA probe spanning the complete open reading frame of Gpihbp1, shows the absence of Gpihbp1 expression in heart and brown adipose tissue (BAT) from Gpihbp1−/− mice. (C) Western blot with a GPIHBP1-specific rabbit antiserum showing GPIHBP1 in brown adipose tissue (BAT) and gonadal fat pad extracts from Gpihbp1+/+ mice but not Gpihbp1−/− mice. As a control, extracts from HeLa cells that had been transfected with an untagged or an S-protein–tagged GPIHBP1 construct were included.
