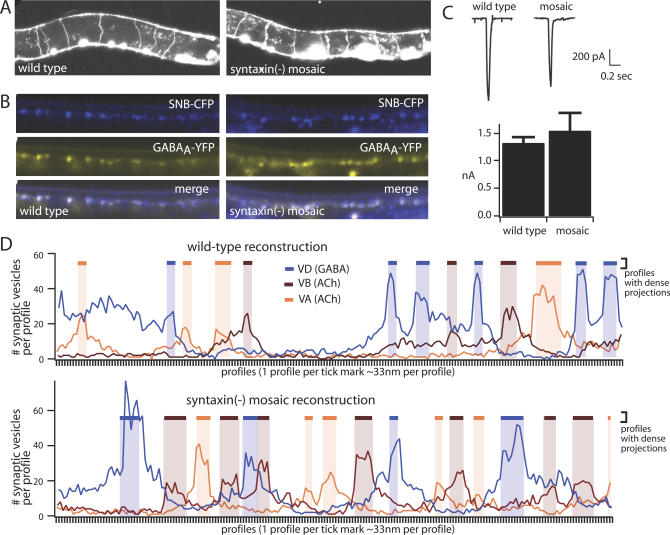
Figure 3. Neurons That Lack Syntaxin Have Normal Morphology.
(A) GABA neuron development is presented. Sample images of wild type and syntaxin mosaic (EG3278) animals expressing GFP in the GABA neurons are shown. Right, anterior; top, dorsal. In both genotypes, commissures extend at regular intervals from the ventral to the dorsal nerve cord. The bright spots along the ventral nerve cord in the wild type are cell bodies. Cell bodies are also visible in the syntaxin mosaic, as are the larger coelomocytes, which express GFP as a marker for the syntaxin mosaic array. The number of commissures between the dorsal and ventral nerve cords is normal in syntaxin mosaic animals. n = 10 adults for each genotype.
(B) Pre- and postsynaptic development is presented. Sample images are shown of the dorsal nerve cord of wild-type and syntaxin mosaic (EG3278) animals coexpressing a presynaptic marker (SNB-CFP, synaptobrevin-CFP,) and a postsynaptic marker (GABAA receptor-YFP). SNB-CFP is expressed in GABA neurons, which lack syntaxin in the mosaic animals. Normal colocalization was observed in both genotypes (n = 10 adults for each genotype).
(C) The postsynaptic receptor field is presented. The postsynaptic response to exogenous GABA is normal in the syntaxin mosaic animals (EG3817) that lack syntaxin in the GABA neurons. Sample traces are shown on the left, and mean and standard error of mean data are shown on the right (n = 4 for each for each genotype).
(D) EM reconstruction of the nerve cord in syntaxin mosaic animals (EG3817) lacking syntaxin in the GABA motor neurons is presented. The number and distribution of presynaptic specializations and of synaptic vesicle number is normal in syntaxin(−) neurons. The line graphs show the number of vesicles in each serial profile for the wild type (top) and the syntaxin mosaic (EG3817, bottom). Three profiles are presented on each graph: VD, blue; VA, brown; and VB, orange. Profiles containing a dense projection are indicated by a shaded bar of the corresponding color. The distribution of the dense projections in GABA syntaxin(−) neurons is similar to the wild-type pattern, with inhibitory and excitatory synapses alternating along the length of the nerve cord. Reconstructions are from 201 serial sections for the wild type and 199 serial sections for the mosaic strain.