Figure 2.
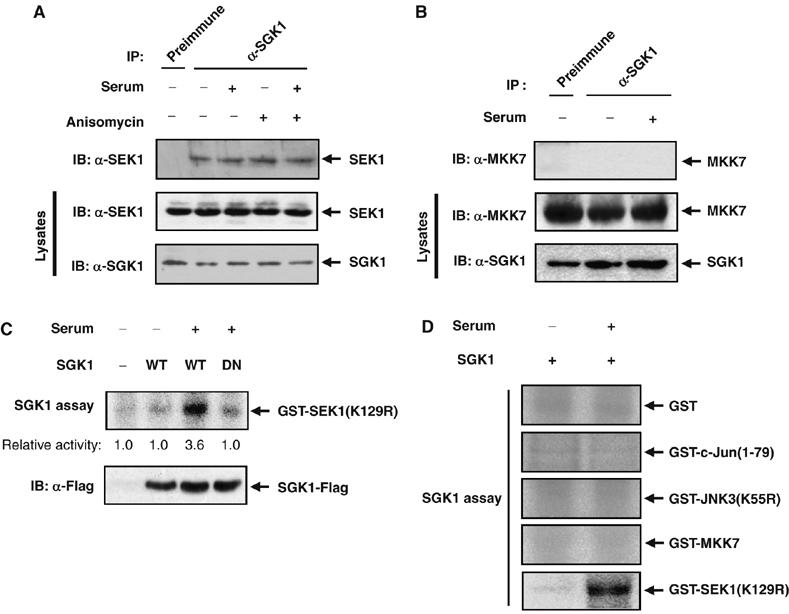
SGK1 physically associates with SEK1. (A) Rat2 cells were deprived of serum for 16 h, incubated for 20 min in the absence or presence of 10% FBS, and then incubated further for 20 min in the absence or the presence of 10 μg/ml anisomycin. Cell lysates were then subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP) with anti-SGK1 or rabbit preimmune IgG, and the resulting precipitates were subjected to immunoblot analysis with anti-SEK1 antibody. Cell lysates were also examined directly by immunoblot analysis with antibodies to SGK1 or to SEK1. (B) Rat2 cells were deprived of serum for 16 h and then incubated for 20 min in the absence or presence of 10% FBS. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-SGK1 or rabbit preimmune IgG, and the resulting precipitates were subjected to immunoblot analysis with anti-MKK7 antibody. Cell lysates were also examined directly by immunoblot analysis with antibodies to SGK1 or to MKK7. (C, D) 293T cells were transfected for 48 h with expression vectors for Flag-tagged wild-type (WT) SGK1 or SGK1-DN (C), or with a vector for wild-type SGK1-Flag (D). The cells were then deprived of serum for 16 h before incubation for 20 min in the absence or presence of 10% FBS. Cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-Flag antibody, and the resulting precipitates were assayed for kinase activity to phosphorylate GST-SEK1 (K129R) (C) or the indicated GST-fusion proteins (D) as substrate.
