Figure 8.
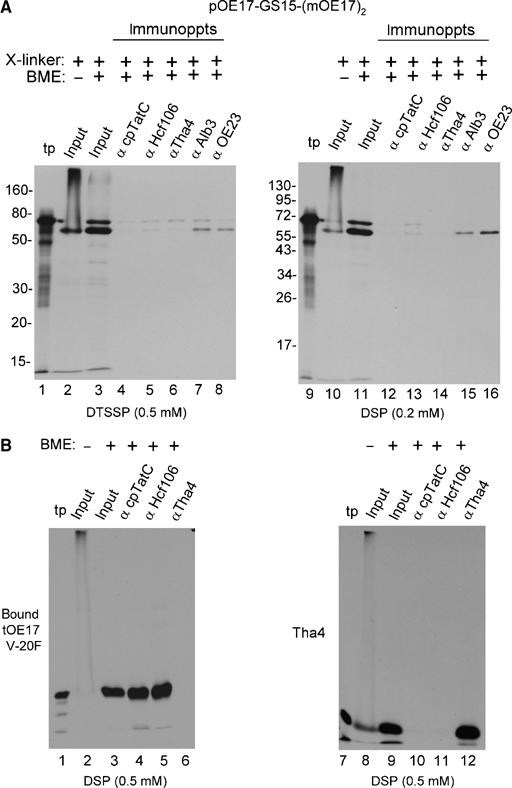
Attempt to identify association of arrested substrates with cpTat components by chemical crosslinking and co-immunoprecipitation. Thylakoids from a transport assay with pOE17-GS15-(mOE17)2, a binding assay with tOE17 V-20F, or an integration assay with Tha4 were subjected to crosslinking with the indicated amounts of DTSSP or DSP (Materials and methods). Thylakoids were recovered, dissolved in 1% SDS, and subjected to immunoprecipitation (Materials and methods). Elution from the antibody beads was with SDS buffer containing β mercaptoethanol (BME) as shown above the panels to break the crosslinker. (A) Immunoprecipitation of crosslinked mOE17-GS15-(mOE17)2 was as designated above the panels. The relative amounts of samples loaded were as follows: translation product (tp, lanes 1 and 9), 4% of the transport assay; the input to the immunoprecipitations in the absence (lanes 2 and 10) or presence (lanes 3 and 11) of BME, 20% of the assay; and the antibody eluates, 100% of the assay. Thermolysin treatment of the thylakoids indicated that 90% of mOE17-GS15-(mOE17)2 was transport arrested. (B) Thylakoid-bound tOE17 V-20F and thylakoid integrated Tha4 were crosslinked with 0.5 mM DSP and subjected to immunoprecipitation with antibody beads as shown above the panels and described in (A). Sample loading was the same as in (A).
