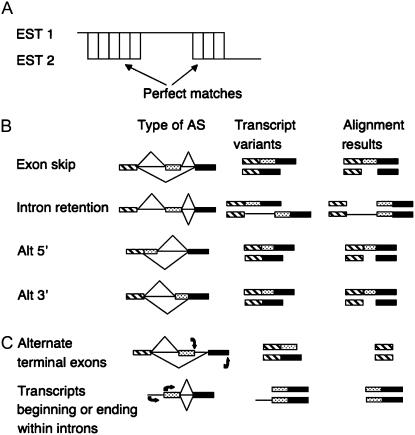
Figure 1.
Schematic diagrams of AS types detected by the EPGA algorithm. A, EPGA showing perfectly matched regions of at least 25 bp that flank a 5 bp or longer indel. B, Types of AS that match the EPGA requirements as shown in A include: exon skipping, alternative 5′ splice donor sites, alternative 3′ splice acceptor sites, and intron retention. AS patterns are represented by (top and bottom) diagonal lines. The AS results in two transcript variants that are shown together with the predicted alignment results. Boxes represent exon sequences and lines represent intron sequences. C, Other types of AS including alternate terminal exons or transcripts beginning or ending within introns that do not match the EPGA alignment requirements. The description is as in B where arrows at the bottom represent start and termination of transcription.