Fig. 4.
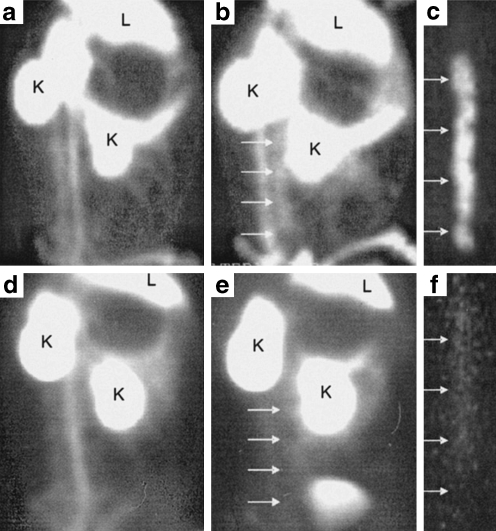
Feasibility of non-invasive imaging of apoptosis by radiolabelled Anx A5. Left lateral oblique gamma images of experimental atherosclerotic (a–c) and control (d–f) rabbits injected with 99mTc-Anx A5; L and K indicate liver and kidney activities, respectively. Images at the time of injection (a, d) and at 2 h after injection (b, e) are shown. Although blood pool activity is seen at the time of injection (a) in the atherosclerotic animal, tracer uptake is clearly visible in the abdominal aorta (with lesions) at 2 h (b). c Ex vivo image of b shows intense 99mTc-Anx A5 uptake in the arch and abdominal region. Annexin-positive areas were confirmed to contain macrophage- and apoptosis-rich regions in the atherosclerotic plaque by histology. d–f show the corresponding images in the control animal. Note that the aorta is indistinguishable from background at 2 h after injection (e). The blood pool at the time of injection in the control animal (d) is comparable to that in the atherosclerotic animal. f Ex vivo aortic image of the control animal demonstrates the absence of 99mTc-labelled Anx A5 uptake. From Kolodgie et al. [75]