Fig. 6.
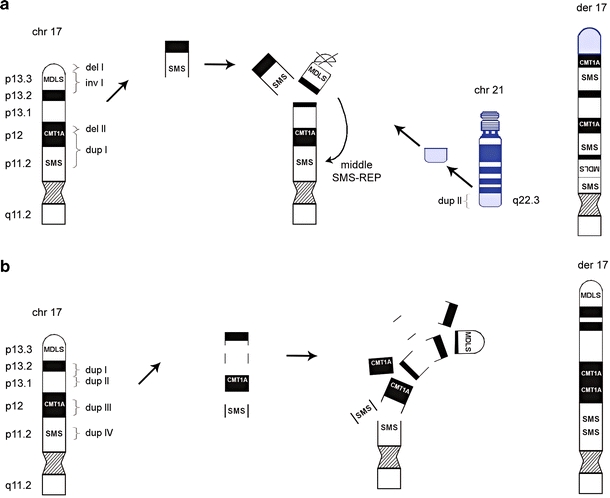
Schematic representation of the proposed mechanism for CCR formation in patient 1 and patient 2. a The complex rearrangement observed in patient 1 includes nine breakpoints, with one insertion, two microdeletions and two microduplications. We propose that the breaks in chromosome 17, p13.3, p12 and p11.2 as well as the break in chromosome 21q22.3 arose simultaneously. This resulted in the insertion of the MDLS region into the middle SMS-REP/LCR17pB block, loss of telomeric 17p and part of 17p12 and duplication of the CMT1A region. Additionally, the duplicated 21q22.3 fragment was translocated to the 17p subtelomeric region. b The complex rearrangement in patient 2 included eight breaks. We suggest that breaks in chromosome 17, p13.2, p13.1, p12 and p11.2 occurred at the same time, resulting in four interspersed directly orientated microduplications. Arrows do not represent a chronological order of events
