Figure 1.
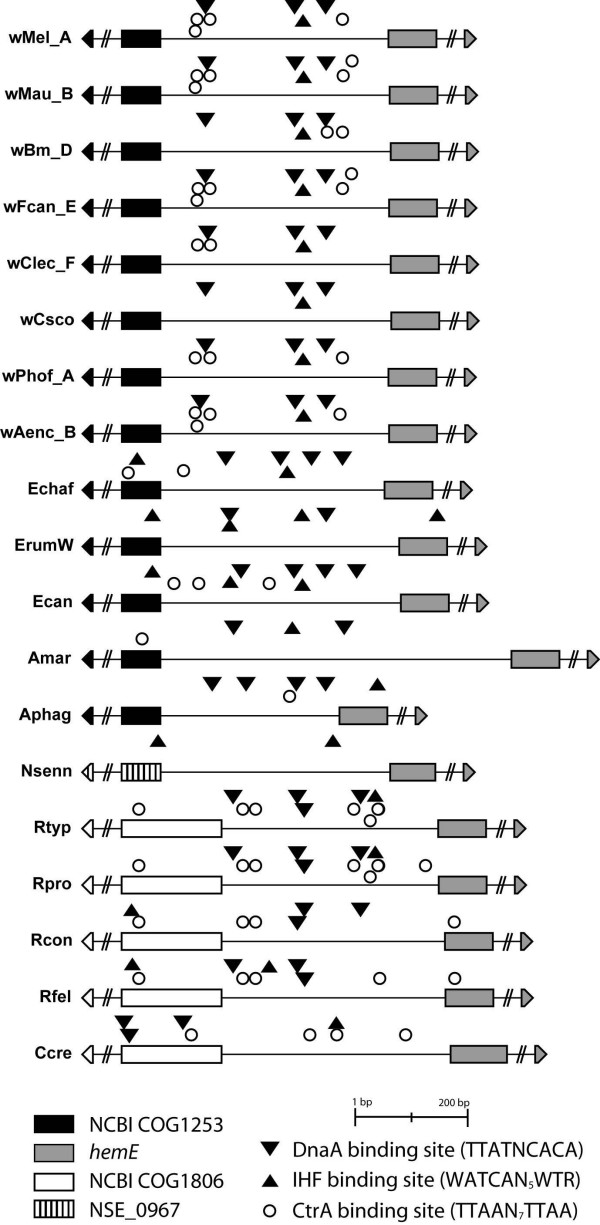
Schematic representation of representative origins of replication. Schematic drawing of ori regions from Wolbachia, Anaplasma, Ehrlichia and Rickettsia. Inverted triangles denote DnaA boxes, circles denote CtrA binding sites and triangles indicate IHF binding sites. The flanking genes are fragmented. Some protein binding sites are located outside ori but within either of the boundary genes; however, the flanking genes were not fully sequenced from the Wolbachia strains of F. candida, C. lectularius, C. scorpioides, P. hoffmeyeri, and A. encedon. Note also that in A. marginale the ori region appears to be significantly longer due to the differently annotated hemE gene (see text for details). wMel_A, Wolbachia of Drosophila melanogaster wMel; wMau_B, Wolbachia of Drosophila mauritiana wMau; wBm_D, Wolbachia of Brugia malayi wBm; wFcan_E, Wolbachia of Folsomia candida wFcanE; wClec_F, Wolbachia of Cimex lectularius wClecF; wCsco, Wolbachia of Cordylochernes scorpioides wCsco; wPhof_A, Wolbachia of Pegoscapus hoffmeyeri wPhofA; wAenc_B, Wolbachia of Acraea encedon wAencB; Echaf, Ehrlichia chaffeensis Arkansas; ErumW, E. ruminantium Welgevonden; Ecan, E. canis Jake; Amar, Anaplasma marginale St Maries; Aphag, A. phagocytophilum HZ; Nsenn, Neorickettsia sennetsu Miyayama; Rtyp, Rickettsia typhi Wilmington; Rpro, R. prowazekii Madrid E; Rcon, R. conorii Malish 7; Rfel, R. felis URRWXCal2; Ccre, Caulobacter crescentus CB15.
