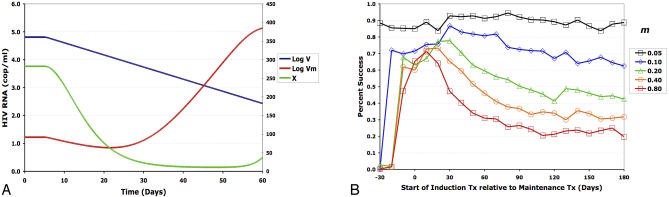
Figure 10. Computer Simulations of Dynamics of Drug-Resistant Virus under Simple Immune-Control Model.
(A) Immune-control analog of the one-cell, one-drug model presented in Figure 4.
(B) Effect of changing turnover rate of immune effectors under the immune-control analog of the full model explored in Figures 5–9. In this simulation, the turnover rate of the immune effectors was modeled by simultaneously increasing s X, m X, and k X. Here, k = 0.00085, T = 1,000, μ = 6 × 10−4, and w 1 = w 2 = w 3 = w 4 = 0.9. Other parameters are as in Table 2.
Interpretation: changing the factor responsible for controlling viral load did not change the conclusion that drug resistant viruses will decrease transient after drug therapy. As with the target-cell limited model, the rate at which the factor that controlled viral load changed after therapy played a major role in determining when therapy should be intensified.