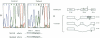Abstract
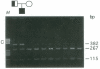
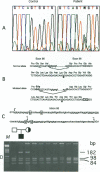
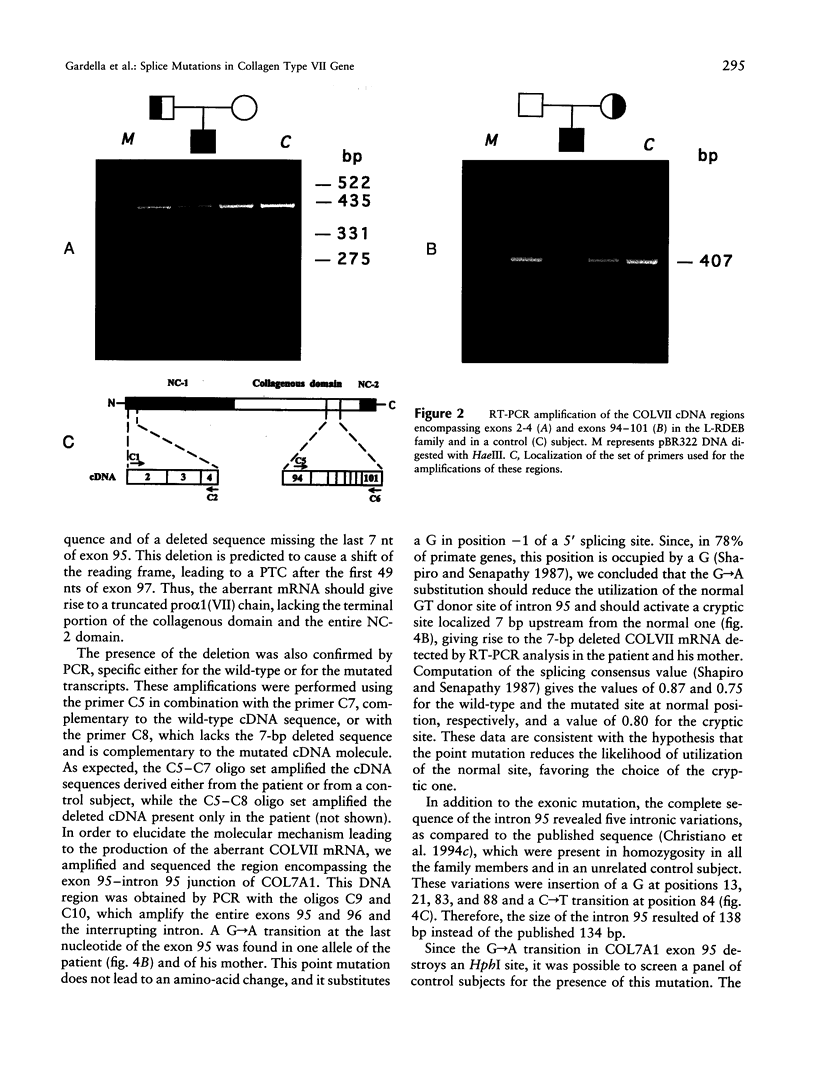
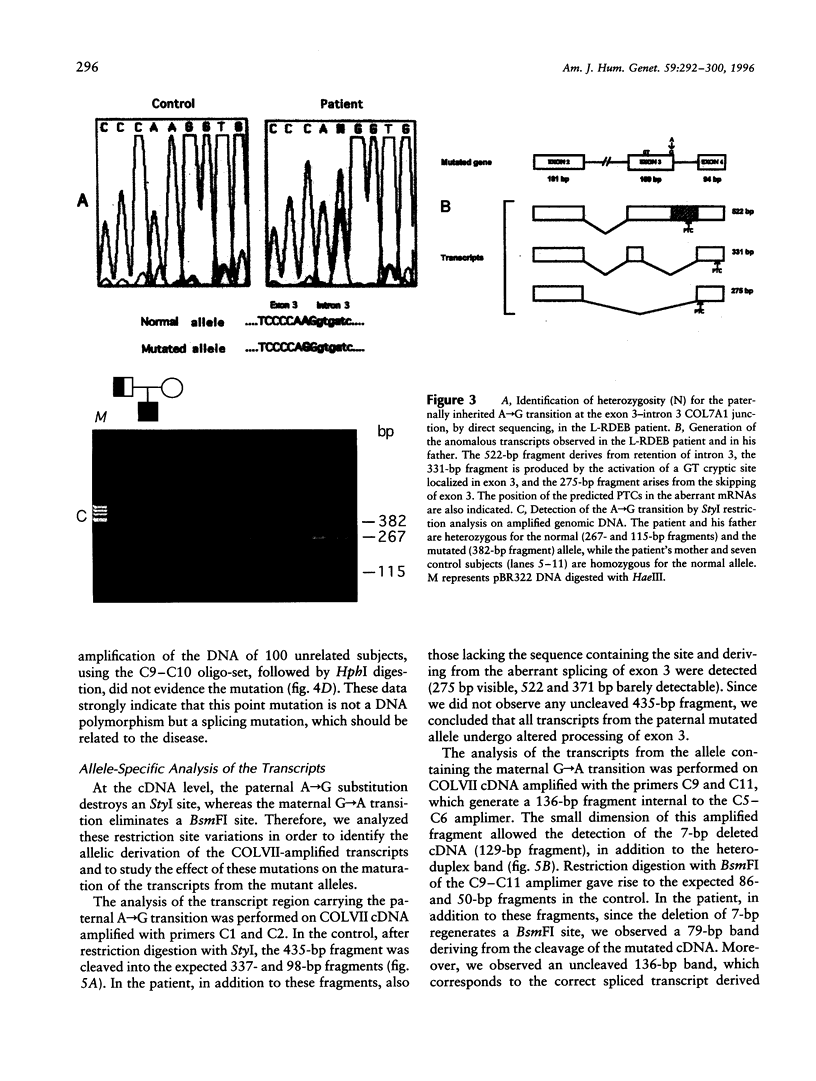
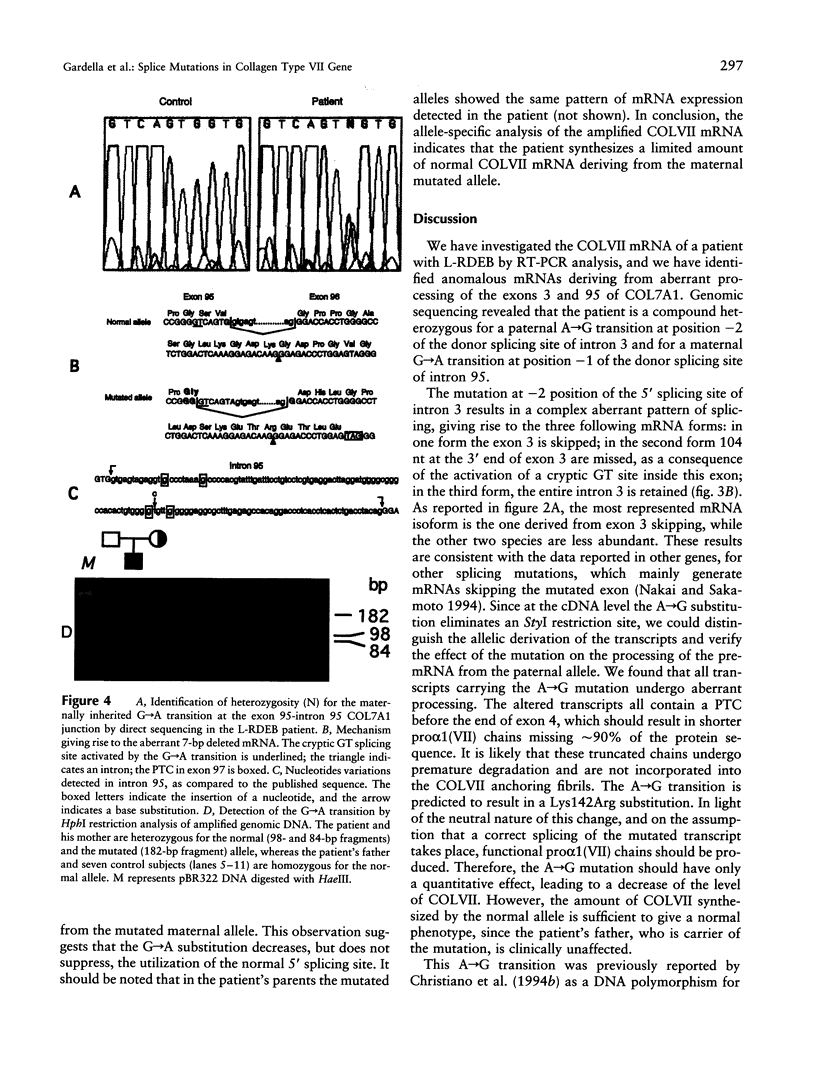
Collagen type VII gene (COL7A1) has been demonstrated to be altered in several variants of dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (DEB), with either recessive or dominant mode of inheritance. We have identified two mutations in a patient affected by a localisata variant of recessive DEB (L-RDEB), which is characterized by the less severe phenotype of the syndrome. These mutations are the first splicing mutations so far described for COL7A1 in DEB. One mutation is a paternally inherited A-->G transition at position -2 of the donor splicing site of intron 3, which results in three aberrant mRNAs, depending on the skipping of exon 3, the usage of a cryptic donor site inside exon 3, or the maintenance of intron 3. The second mutation is a maternally inherited G-->A transition at position -1 of the donor splicing site of intron 95, which induces the activation of a cryptic donor site 7 nt upstream the normal site and gives rise to a deleted mRNA, in addition to the normal one. All aberrant mRNAs show a shift of the reading frame, thus generating premature termination codons of translation. Allele-specific analysis of the transcripts has shown that the maternal mutation does not completely abolish the correct splicing of COLVII pre-mRNA, thus allowing, in the patient, the synthesis of a certain level of a functional protein. This result is compatible with the mild clinical L-RDEB phenotype observed in our patient.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bruckner-Tuderman L., Rüegger S., Odermatt B., Mitsuhashi Y., Schnyder U. W. Lack of type VII collagen in unaffected skin of patients with severe recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. Dermatologica. 1988;176(2):57–64. doi: 10.1159/000248673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christiano A. M., Anhalt G., Gibbons S., Bauer E. A., Uitto J. Premature termination codons in the type VII collagen gene (COL7A1) underlie severe, mutilating recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. Genomics. 1994 May 1;21(1):160–168. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christiano A. M., Greenspan D. S., Hoffman G. G., Zhang X., Tamai Y., Lin A. N., Dietz H. C., Hovnanian A., Uitto J. A missense mutation in type VII collagen in two affected siblings with recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. Nat Genet. 1993 May;4(1):62–66. doi: 10.1038/ng0593-62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christiano A. M., Greenspan D. S., Lee S., Uitto J. Cloning of human type VII collagen. Complete primary sequence of the alpha 1(VII) chain and identification of intragenic polymorphisms. J Biol Chem. 1994 Aug 12;269(32):20256–20262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christiano A. M., Hoffman G. G., Chung-Honet L. C., Lee S., Cheng W., Uitto J., Greenspan D. S. Structural organization of the human type VII collagen gene (COL7A1), composed of more exons than any previously characterized gene. Genomics. 1994 May 1;21(1):169–179. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christiano A. M., Rosenbaum L. M., Chung-Honet L. C., Parente M. G., Woodley D. T., Pan T. C., Zhang R. Z., Chu M. L., Burgeson R. E., Uitto J. The large non-collagenous domain (NC-1) of type VII collagen is amino-terminal and chimeric. Homology to cartilage matrix protein, the type III domains of fibronectin and the A domains of von Willebrand factor. Hum Mol Genet. 1992 Oct;1(7):475–481. doi: 10.1093/hmg/1.7.475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christiano A. M., Suga Y., Greenspan D. S., Ogawa H., Uitto J. Premature termination codons on both alleles of the type VII collagen gene (COL7A1) in three brothers with recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. J Clin Invest. 1995 Mar;95(3):1328–1334. doi: 10.1172/JCI117783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunnill M. G., Richards A. J., Milana G., Mollica F., Eady R. A., Pope F. M. A novel homozygous point mutation in the collagen VII gene (COL7A1) in two cousins with recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Sep;3(9):1693–1694. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.9.1693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandchamp B., Picat C., de Rooij F., Beaumont C., Wilson P., Deybach J. C., Nordmann Y. A point mutation G----A in exon 12 of the porphobilinogen deaminase gene results in exon skipping and is responsible for acute intermittent porphyria. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 25;17(16):6637–6649. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.16.6637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenspan D. S. The carboxyl-terminal half of type VII collagen, including the non-collagenous NC-2 domain and intron/exon organization of the corresponding region of the COL7A1 gene. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Mar;2(3):273–278. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.3.273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilal L., Rochat A., Duquesnoy P., Blanchet-Bardon C., Wechsler J., Martin N., Christiano A. M., Barrandon Y., Uitto J., Goossens M. A homozygous insertion-deletion in the type VII collagen gene (COL7A1) in Hallopeau-Siemens dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. Nat Genet. 1993 Nov;5(3):287–293. doi: 10.1038/ng1193-287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz D. S., Krainer A. R. Mechanisms for selecting 5' splice sites in mammalian pre-mRNA splicing. Trends Genet. 1994 Mar;10(3):100–106. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(94)90233-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovnanian A., Duquesnoy P., Blanchet-Bardon C., Knowlton R. G., Amselem S., Lathrop M., Dubertret L., Uitto J., Goossens M. Genetic linkage of recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa to the type VII collagen gene. J Clin Invest. 1992 Sep;90(3):1032–1036. doi: 10.1172/JCI115916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovnanian A., Hilal L., Blanchet-Bardon C., de Prost Y., Christiano A. M., Uitto J., Goossens M. Recurrent nonsense mutations within the type VII collagen gene in patients with severe recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. Am J Hum Genet. 1994 Aug;55(2):289–296. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaler S. G., Gallo L. K., Proud V. K., Percy A. K., Mark Y., Segal N. A., Goldstein D. S., Holmes C. S., Gahl W. A. Occipital horn syndrome and a mild Menkes phenotype associated with splice site mutations at the MNK locus. Nat Genet. 1994 Oct;8(2):195–202. doi: 10.1038/ng1094-195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keene D. R., Sakai L. Y., Lunstrum G. P., Morris N. P., Burgeson R. E. Type VII collagen forms an extended network of anchoring fibrils. J Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;104(3):611–621. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.3.611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krawczak M., Reiss J., Cooper D. N. The mutational spectrum of single base-pair substitutions in mRNA splice junctions of human genes: causes and consequences. Hum Genet. 1992 Sep-Oct;90(1-2):41–54. doi: 10.1007/BF00210743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemmink H. H., Kluijtmans L. A., Brunner H. G., Schröder C. H., Knebelmann B., Jelínková E., van Oost B. A., Monnens L. A., Smeets H. J. Aberrant splicing of the COL4A5 gene in patients with Alport syndrome. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Feb;3(2):317–322. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.2.317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrath J. A., Ishida-Yamamoto A., O'Grady A., Leigh I. M., Eady R. A. Structural variations in anchoring fibrils in dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa: correlation with type VII collagen expression. J Invest Dermatol. 1993 Apr;100(4):366–372. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12471830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh I., Hamosh A., Dietz H. C. Nonsense mutations and diminished mRNA levels. Nat Genet. 1993 Jul;4(3):219–219. doi: 10.1038/ng0793-219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakai K., Sakamoto H. Construction of a novel database containing aberrant splicing mutations of mammalian genes. Gene. 1994 Apr 20;141(2):171–177. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(94)90567-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryynänen M., Knowlton R. G., Parente M. G., Chung L. C., Chu M. L., Uitto J. Human type VII collagen: genetic linkage of the gene (COL7A1) on chromosome 3 to dominant dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Oct;49(4):797–803. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryynänen M., Ryynänen J., Sollberg S., Iozzo R. V., Knowlton R. G., Uitto J. Genetic linkage of type VII collagen (COL7A1) to dominant dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa in families with abnormal anchoring fibrils. J Clin Invest. 1992 Mar;89(3):974–980. doi: 10.1172/JCI115680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro M. B., Senapathy P. RNA splice junctions of different classes of eukaryotes: sequence statistics and functional implications in gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 11;15(17):7155–7174. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.17.7155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidaud M., Gattoni R., Stevenin J., Vidaud D., Amselem S., Chibani J., Rosa J., Goossens M. A 5' splice-region G----C mutation in exon 1 of the human beta-globin gene inhibits pre-mRNA splicing: a mechanism for beta+-thalassemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):1041–1045. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.1041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil D., D'Alessio M., Ramirez F., Steinmann B., Wirtz M. K., Glanville R. W., Hollister D. W. Temperature-dependent expression of a collagen splicing defect in the fibroblasts of a patient with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type VII. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 5;264(28):16804–16809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]