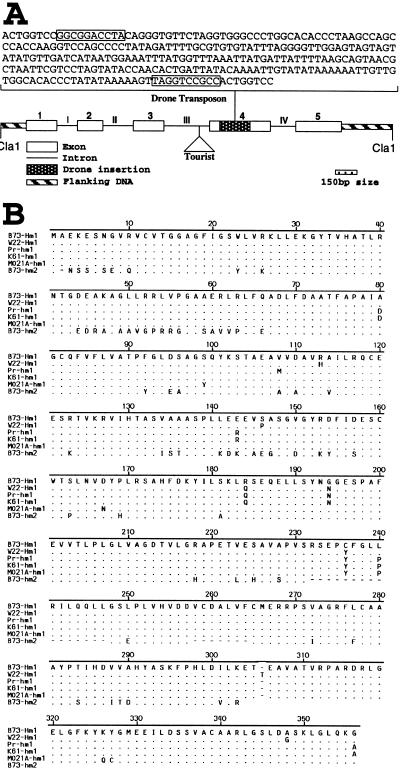
Figure 2.
(A) Structural representation of hm1-Pr showing exons, introns, and two insertions, Tourist and Drone. The entire sequence of Drone (256 bp) is shown with its 10-bp terminal-inverted repeats boxed. The sequences that flank the terminal-inverted repeats represent the 8-bp duplication at the site of insertion. (B) Comparison of the deduced amino acid sequences of cDNA clones of Hm1-B73 and Hm1-W22 (two wild-type alleles of Hm1) with that of the corresponding sequence from the hm1-Pr, hm1-K61, hm1-MO21A, and hm2-B73 genomic clones. Drone insertion and the 8-bp sequence site duplication are not included in the translation products of the hm1-Pr and hm1-K61 sequences. Letters represent amino acids. In the predicted translation products of W22, Pr, K61, MO21A, and hm2-B73, only those amino acids that differ from Hm1-B73 have been shown by letter designations; identical and missing amino acids are shown by dots and dashes, respectively. The 3′ nonmatching sequence of hm2-B73, whose exon and intron boundaries are the same as hm1, is omitted. The complete sequences of W22-Hm1, Pr-hm1, K61-hm1, Mo21-hm1, and B73-hm2 have been deposited in GenBank, accession numbers AF041043, AF041044, AF041045, AF041046, and AF041047, respectively.