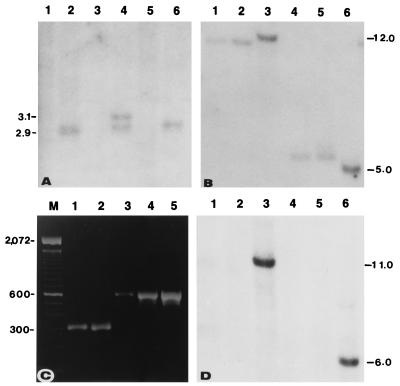
Figure 3.
(A) Restriction pattern of DNA from Pr (odd-numbered lanes) and the Hm2 tester (even-numbered lanes) showing deletion of parts of the recessive hm2-Pr allele corresponding to probe HM215. DNA of lanes 1 and 2, 3 and 4, and 5 and 6 were digested with SacI, XhoI, and HindIII, respectively. (B) A Southern blot of DNAs from Pr (lanes 1 and 4), K61 (lanes 2 and 5), and MO21A (lanes 3 and 6) inbreds, was digested with EcoRI (lanes 1–3) and SstI (lanes 4–6) and hybridized with a 0.9-kb SstI/XhoI fragment of Hm1. (C) PCR-amplified products from the genomic DNA of inbreds B73 (lane 1), MO21A (lane 2), Pr (lane 3), and K61 (lane 4) and from the pHMC5 subclone of hm1-Pr (lane 5). Lane M contains the 100-bp ladder. The 567-bp amplification product is diagnostic for the presence of the Drone insertion; in the absence of Drone, an amplification product of ≈311 bp is obtained. (D) Southern hybridization of the blot used in B with HM215, revealing the lack of the hm2 deletion, characteristic of Pr and K61, in MO21A.