Table 2.
Composition of the disaccharides of various glycosaminoglycan chains
| Heparan sulfate | Chondroitin sulfate | Dermatan sulfatea | Hyaluronan | Keratan sulfate | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Uronic acid | GlcA(2S) IdoA(2S) | GlcA | GlcA IdoA(2S) | GlcA | Gal(6S) |
| Disaccharide link | 1β4 | 1β3 | 1β3 | 1β3 | 1β4 |
| Hexosamine | GlcNAc(NS)(3S)(6S) | GalNAc4Sa GalNAc6Sa | GalNAc(4S)(6S) | GlcNAc | GlcNAc(6S) |
| Polymerization link | 1β4 | 1β4 | 1β4 | 1β4 | 1β3 |
Note the various possibilities of sulfation in heparan sulfate. These may coincide (e.g., in heparan sulfate the hexosamine GlcNS3S). A rare but possible hexosamine in heparan sulfate is the N-unsubstituted glucosamine 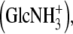 which has been left out of the table for convenient reading. Also note the presence of IdoA in dermatan sulfate, in contrast to the other chondroitin sulfates, making it more alike to heparan sulfate.
which has been left out of the table for convenient reading. Also note the presence of IdoA in dermatan sulfate, in contrast to the other chondroitin sulfates, making it more alike to heparan sulfate.
GlcA Glucuronic acid, IdoA iduronic acid, Gal galacturonic acid, GlcNAc N-acetyl-glucosamine, GalNAc N-acetyl-galactosamine, 2S 2-O-sulfated, 3S 3-O-sulfated, 4S 4-O-sulfated, 6S 6-O-sulfated, NS N-sulfated
aThere are three types of chondroitin sulfate. Type A only has 4-O-sulfated N-acetyl-galactosamines, type B is known as dermatan sulfate and type C only has 6-O-sulfated N-acetyl-galactosamines.
