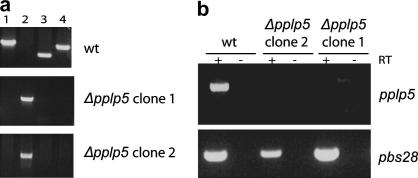
Fig. 2.
Generation of Δpplp5 parasites. Generation of constructs for targeted disruption of pplp5 by double homologous recombination were carried out as previously described (Dessens et al., 1999). Briefly, an upstream homology region of 469 bp was PCR amplified from Plasmodium berghei ANKA clone 2.34 genomic DNA using primers AE27A (5′-TTGGGCCCGTTGAATATGCATAGACAACATC-3′) and AE27B (5′-CCAAGCTTTCACAAATATAGGCTACTCTTGC-3′) and cloned into pBS-DHFR via ApaI and HindIII (restriction sites in bold). A downstream homology region of 570 bp was PCR amplified using primers AE27C (5′-TGAATTCTCATATTGAATAGGCCTTATATC-3′) and AE27D (5′-GGGGATCCTTTATCACTTCATATCCCAATAC-3′) and cloned into the plasmid with the upstream homology region via EcoRI and BamHI. The targeting cassette was released by ApaI and BamHI digestion. Parasite transfection using the Human T Cell Nucleofector Kit (amaxa), selection by pyrimethamine and dilution cloning were carried out as previously described (Waters et al., 1997; Janse et al., 2006). Diagnostic PCR (a) on genomic DNA from two independent Δpplp clones and control wt parasites. PCRs in lane 1 (27KO 5′-TTAGAATATTTTAAGCATTGGCTATC-3′ and 27WT 5′-CAAATGCCAACCAAATGCAC-3′), 3 (N-ter F and N-ter R) and 4 (MACPF-F 5′-TGAATTCGACCCATTTTTTATAAATATGTTGAA-3′ and MACPF-R 5′-TTCTCGAGTTAGCTAGAATAATATTCTAGAGCT-3′) are specific for the wt allele. The PCR in lane 2 is specific for integration of the gene targeting cassette (primers 27KO and 248 5′-GATGTGTTATGTGATTAATTCATACAC-3′). RT-PCR analysis (b) of pplp expression on total RNA isolated from purified in vitro cultivated ookinetes demonstrates absence of transcript in the Δpplp5 clones. pplp5 primers as in Fig. 1, p28F (5′-GCGAGATCTATGAATTTTAAATACAGTTTTATTTTTTTA-3′) and p28R (5′-GCGCCTAGCATTACTATCACGTAAATAACAAGTA-3′) amplify the pbs28 gene (642 bp).