Abstract
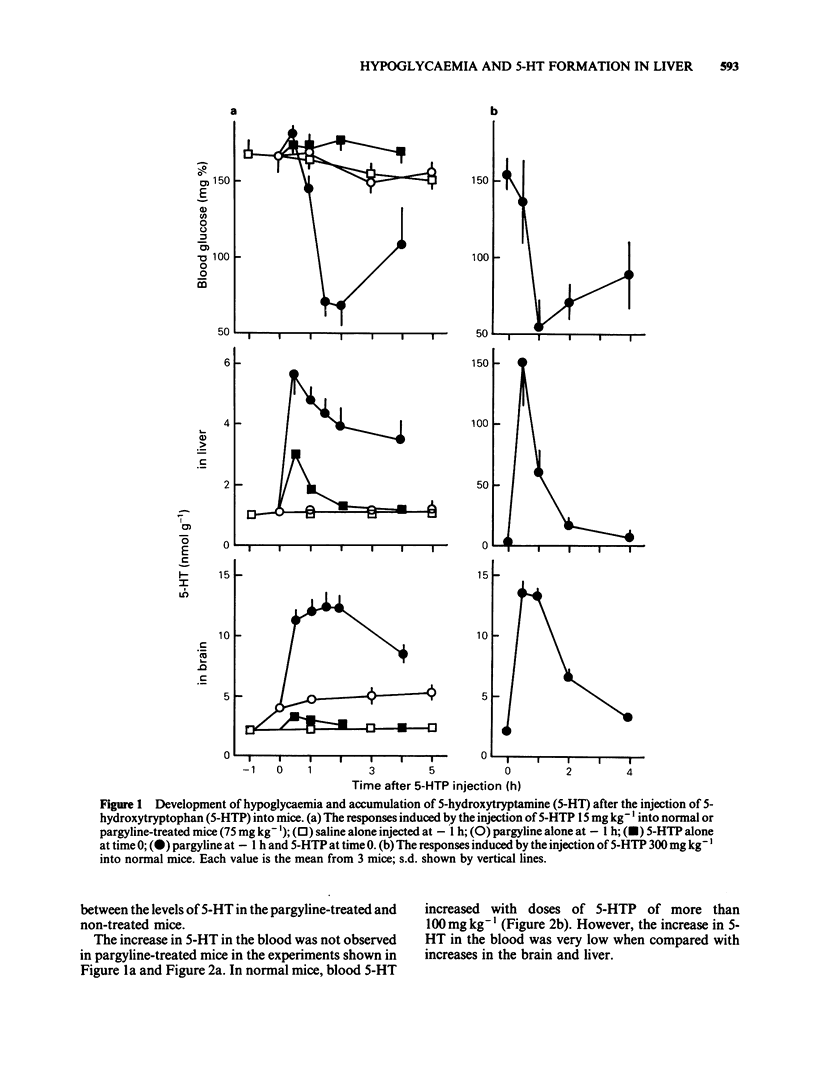
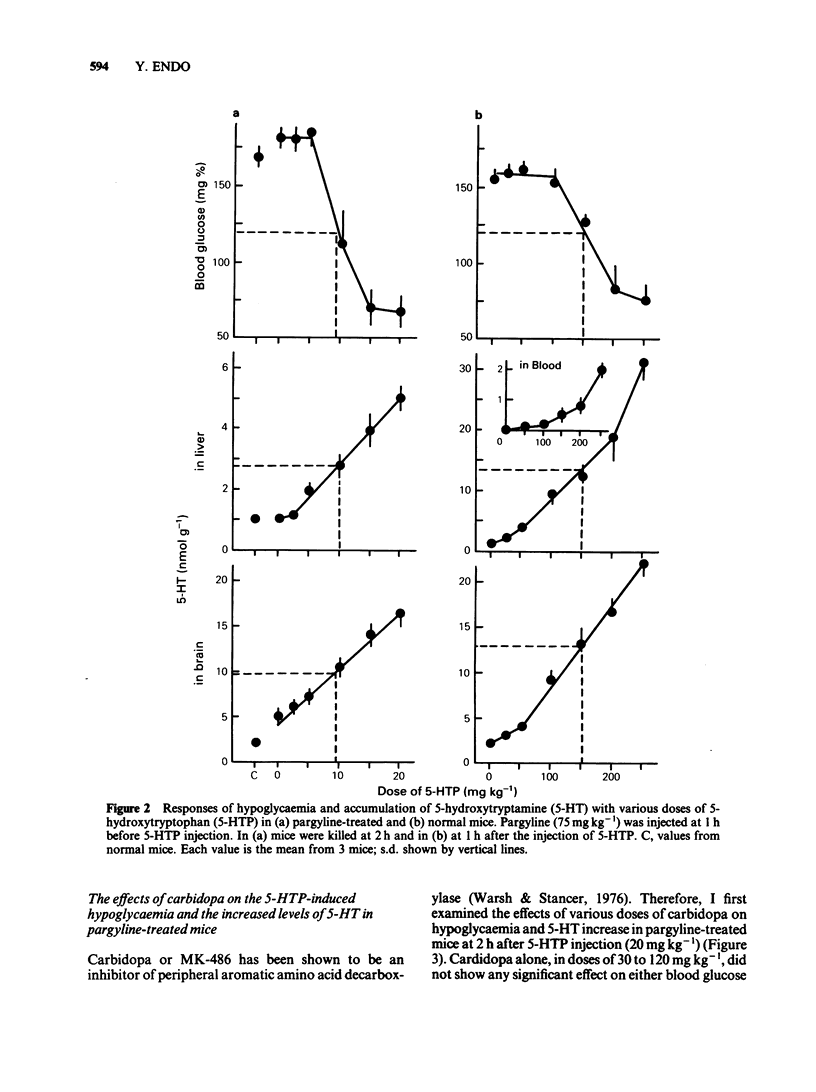
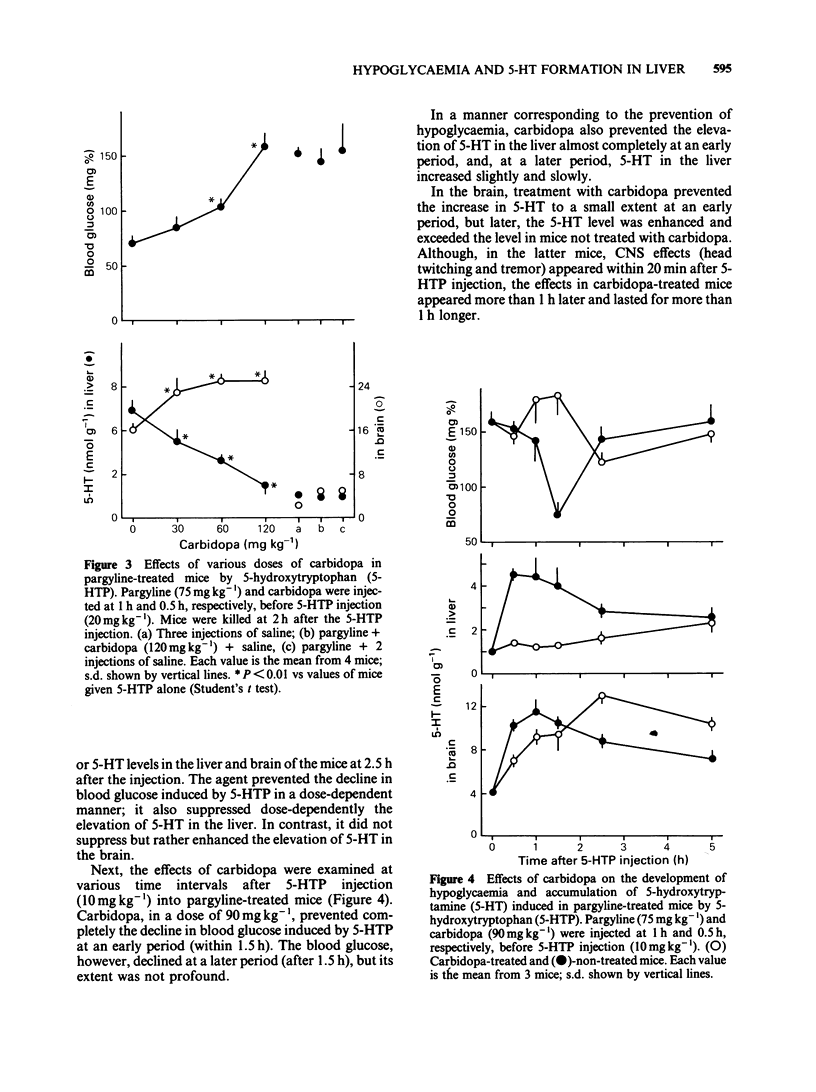
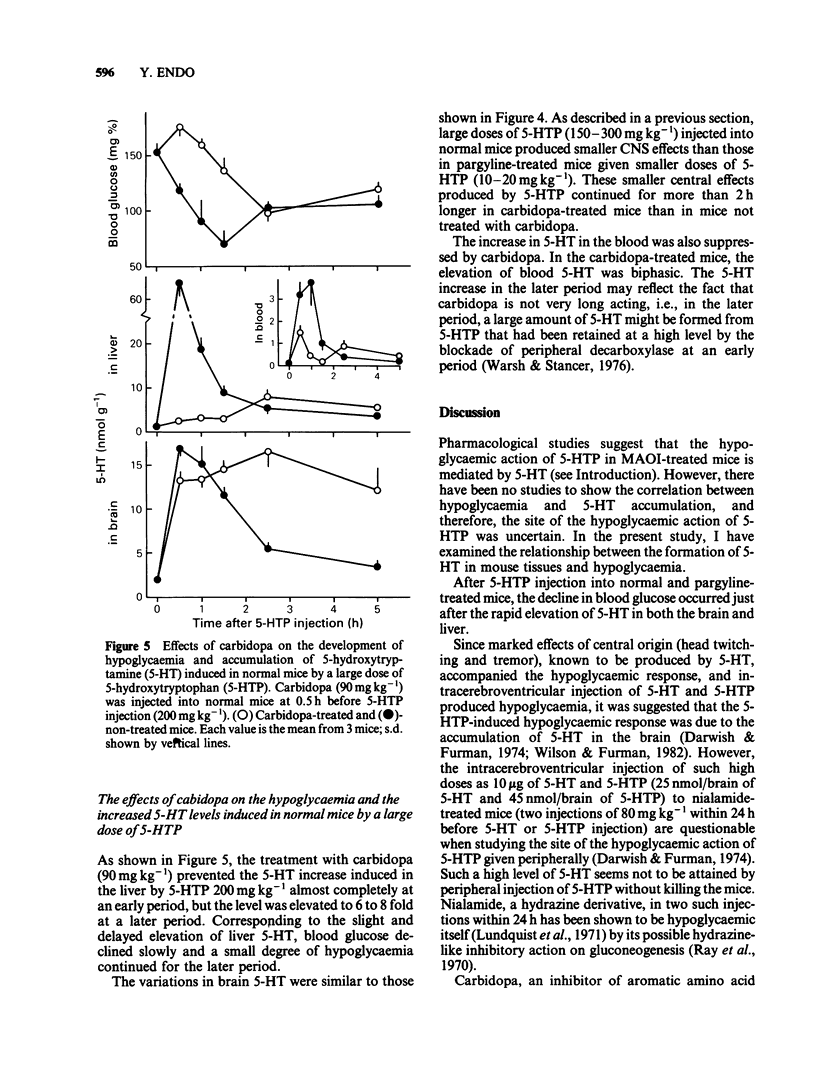
Experiments were undertaken to determine whether the site of the hypoglycaemic action of 5-hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP), a direct precursor of 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), was in the central nervous system or in the liver. The fall in blood glucose followed the rapid increase in the amount of 5-HT both in the brain and liver after 5-HTP injection into pargyline-treated and non-treated mice. Carbidopa, an inhibitor of peripheral aromatic amino acid decarboxylase, prevented the elevation of 5-HT levels in the liver of both pargyline-treated and non-treated mice. In contrast, carbidopa did not prevent but rather enhanced the elevation of 5-HT levels in the brain of both groups of mice. Corresponding to the prevention of 5-HT elevation in the liver, the fall in blood glucose was prevented by carbidopa. These results support the idea that the accumulation of 5-HT in the liver but not in the brain causes the hypoglycaemia induced by 5-HTP.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Darwish S. A., Furman B. L. Medication of the hypoglycaemic effect of 5-hydroxytryptophan by a central nervous system action. Experientia. 1974 Nov 15;30(11):1306–1307. doi: 10.1007/BF01945199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo Y. A lipopolysaccharide and concanavalin A induce variations of serotonin levels in mouse tissues. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 Aug 5;91(4):493–499. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90175-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo Y. Induction of hypoglycaemia and accumulation of 5-hydroxytryptamine in the liver after the injection of mitogenic substances into mice. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Apr;81(4):645–650. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb16130.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filkins J. P., Cornell R. P. Depression of hepatic gluconeogenesis and the hypoglycemia of endotoxin shock. Am J Physiol. 1974 Oct;227(4):778–781. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1974.227.4.778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furman B. L. The hypoglycaemic effect of 5-hydroxytryptophan. Br J Pharmacol. 1974 Apr;50(4):575–580. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1974.tb08591.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furman B. L., Wilson G. A. Further studies on the effects of 5-hydroxytryptophan on plasma glucose and insulin in the mouse. Diabetologia. 1980 Oct;19(4):386–390. doi: 10.1007/BF00280525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd P., Smith S. A., Stribling D., Pogson C. I. Factors affecting tryptophan-induced hypoglycaemia in rats. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 Nov 15;31(22):3563–3569. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90576-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd P., Stribling D., Pogson C. I. Endotoxin and tryptophan-induced hypoglycaemia in rats. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 Nov 15;31(22):3571–3576. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90577-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundquist I., Ekholm R., Ericson L. E. Monoamines in the pancreatic islets of the mouse. 5-hydroxytryptamine as an intracellular modifier of insulin secretion, and the hypoglycaemic action of monoamine oxidase inhibitors. Diabetologia. 1971 Dec;7(6):414–422. doi: 10.1007/BF01212056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCallum R. E., Berry L. J. Effects of endotoxin on gluconeogenesis, glycogen synthesis, and liver glycogen synthase in mice. Infect Immun. 1973 Apr;7(4):642–654. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.4.642-654.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray P. D., Hanson R. L., Lardy H. A. Inhibition by hydrazine of gluconeogenesis in the rat. J Biol Chem. 1970 Feb 25;245(4):690–696. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. H., Porte D., Jr Neuropharmacology of the pancreatic islets. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1976;16:269–285. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.16.040176.001413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. A., Carr F. P., Pogson C. I. The metabolism of L-tryptophan by isolated rat liver cells. Quantification of the relative importance of, and the effect of nutritional status on, the individual pathways of tryptophan metabolism. Biochem J. 1980 Nov 15;192(2):673–686. doi: 10.1042/bj1920673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. A., Elliott K. R., Pogson C. I. Differential effects of tryptophan on glucose synthesis in rats and guinea pigs. Biochem J. 1978 Dec 15;176(3):817–825. doi: 10.1042/bj1760817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. A., Elliott K. R., Pogson C. I. Inhibition of hepatic gluconeogenesis by tryptophan metabolites in rats and guinea pigs. Biochem Pharmacol. 1979 Jul 15;28(14):2145–2148. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(79)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. A., Pogson C. L. Tryptophan and the control of plasma glucose concentrations in the rat. Biochem J. 1977 Dec 15;168(3):495–506. doi: 10.1042/bj1680495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tadano T., Endo Y., Kisara K. A simple determination of serotonin, 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid and 5-hydroxytryptophan decarboxylase activity in rat brain areas and parallel correlation among the levels. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1980 Jun;30(3):347–356. doi: 10.1254/jjp.30.347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UDENFRIEND S., WEISSBACH H., BOGDANSKI D. F. Increase in tissue serotonin following administration of its precursor 5-hydroxytryptophan. J Biol Chem. 1957 Feb;224(2):803–810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warsh J. J., Stancer H. C. Brain and peripheral metabolism of 5-hydroxytryptophan-14C following peripheral decarboxylase inhibition. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1976 Jun;197(3):545–555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson G. A., Furman B. L. Effects of inhibitors of 5-hydroxytryptamine uptake on plasma glucose and their interaction with 5-hydroxytryptophan in producing hypoglycaemia in mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 Mar 12;78(3):263–270. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90027-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


