Abstract
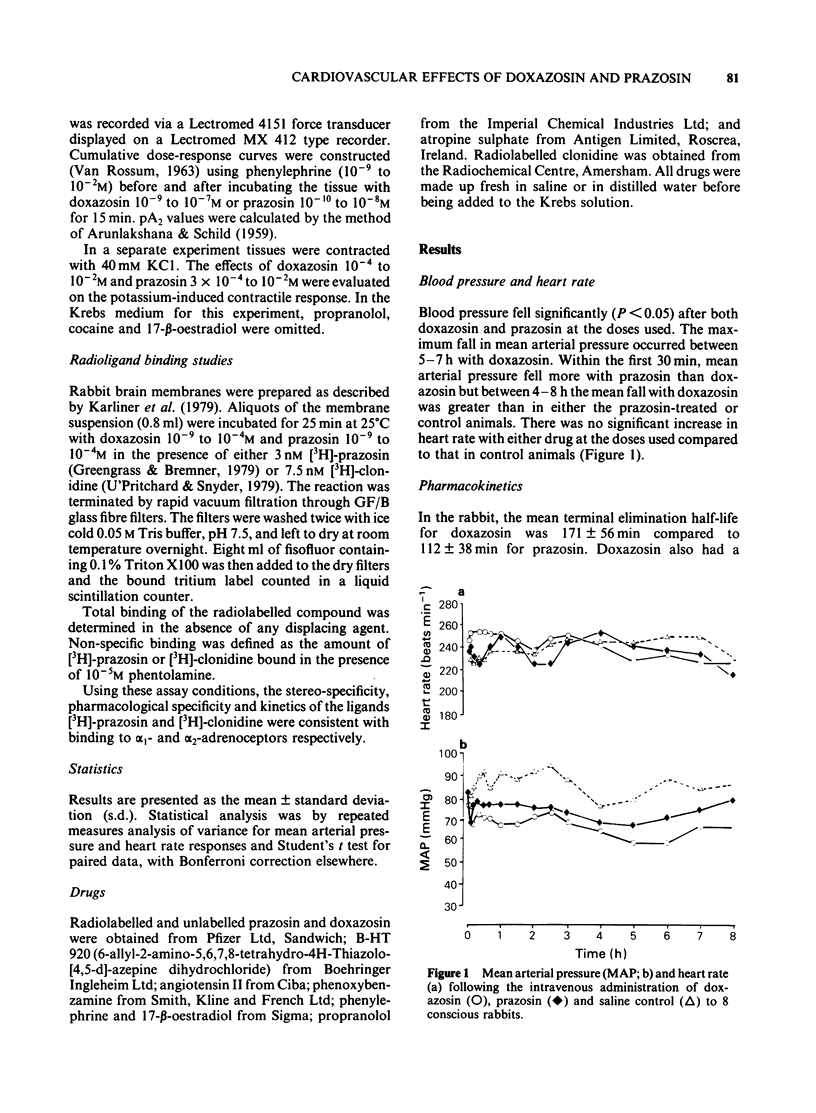
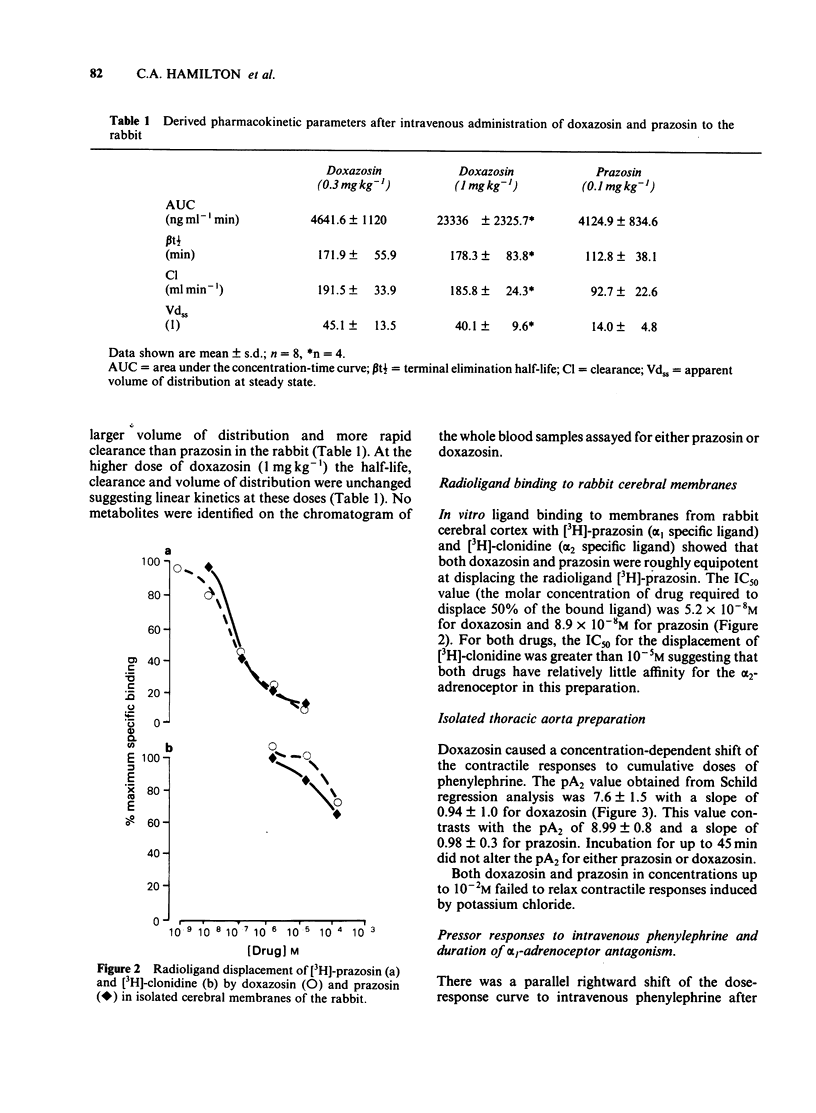
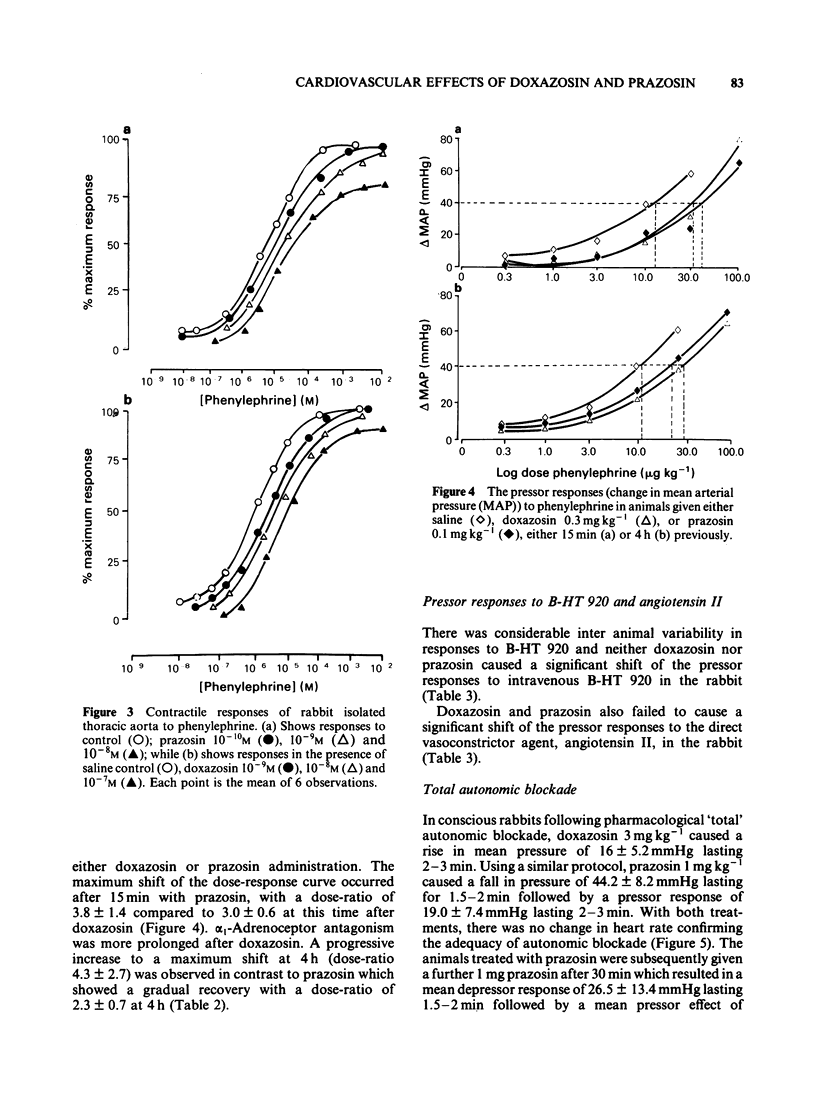
The cardiovascular effects of doxazosin, a quinazoline derivative related to prasozin were investigated and compared to prazosin in the rabbit. Radioligand binding studies using rabbit cerebral membranes showed that both doxazosin and prazosin were roughly equipotent at displacing [3H]-prazosin from specific binding sites. However, the lower pA2 value for doxazosin at alpha 1-adrenoceptors in isolated thoracic aorta preparations suggests a lower potency compared to prazosin. The dose-related pressor effects of intravenous phenylephrine were used to assess vascular alpha 1-adrenoceptor antagonism in vivo. There was a close agreement between alpha 1-adrenoceptor antagonist potency and maximum hypotensive effects with both doxazosin and prazosin. The alpha 1-adrenoceptor antagonist effects of doxazosin were more prolonged than those of prazosin. Studies using either radioligand binding or pressor responses to B-HT 920 showed that doxazosin did not show any significant affinity for the alpha 2-adrenoceptor. Similarly, no direct vasodilator effects were observed either in animals administered angiotensin II or in isolated thoracic aorta spiral strip preparations contracted with potassium. Doxazosin has a longer terminal elimination half-life than prazosin. The pharmacokinetics of doxazosin were linear over the dose range examined. Following pharmacological 'autonomic blockade' and treatment with prazosin, doxazosin did not cause any further fall in blood pressure. These observations suggest that doxazosin, like prazosin, appears to exert its hypotensive action through alpha 1-adrenoceptor antagonism. The prolonged fall in blood pressure and well sustained alpha 1-adrenoceptor antagonism after doxazosin raise the possibility of an active metabolite which also has alpha 1-adrenoceptor blocking properties.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARUNLAKSHANA O., SCHILD H. O. Some quantitative uses of drug antagonists. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1959 Mar;14(1):48–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1959.tb00928.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ali F. K., Kossen S. P., Timmermans P. B., Van Zwieten P. A. Effects of prazosin and two of its derivatives (UK 18.596 and UK 33.274) on alpha-adrenoceptors [proceedings]. Br J Pharmacol. 1980 Jan;68(1):113P–113P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angus J. A., Lew M. J. Phentolamine--an unexpected agonist in the rabbit. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Mar;81(3):423–425. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb10094.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Constantine J. W., Lebel W. Complete blockade by phenoxybenzamine of alpha 1- but not of alpha 2-vascular receptors in dogs and the effects of propranolol. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1980 Nov;314(2):149–156. doi: 10.1007/BF00504531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Docherty J. R., McGrath J. C. A comparison of pre- and post-junctional potencies of several alpha-adrenoceptor agonists in the cardiovascular system and anococcygeus muscle of the rat. Evidence for two types of post-junctional alpha-adrenoceptor. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1980 Jun;312(2):107–116. doi: 10.1007/BF00569718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downing O. A., Wilson K. A., Wilson V. G. Non-competitive antagonism of the alpha-adrenoceptor-mediated fast component of contraction of rat aorta, by doxazosin and prazosin. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Oct;80(2):315–322. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb10036.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew G. M., Whiting S. B. Evidence for two distinct types of postsynaptic alpha-adrenoceptor in vascular smooth muscle in vivo. Br J Pharmacol. 1979 Oct;67(2):207–215. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1979.tb08668.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott H. L., Meredith P. A., Sumner D. J., McLean K., Reid J. L. A pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic assessment of a new alpha-adrenoceptor antagonist, doxazosin (UK33274) in normotensive subjects. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1982 May;13(5):699–703. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1982.tb01439.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott H. L., Reid J. L. Evidence for postjunctional vascular alpha 2-adrenoceptors in peripheral vascular regulation in man. Clin Sci (Lond) 1983 Sep;65(3):237–241. doi: 10.1042/cs0650237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erker E. F., Chan W. Y. The site and the mechanism of phenoxy-benzamine potentiation of the pressor response to oxytocin and vasopressin: in vivo and isolated aortic strips studies. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1977 Aug;202(2):287–293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FURCHGOTT R. F., BHADRAKOM S. Reactions of strips of rabbit aorta to epinephrine, isopropylarterenol, sodium nitrite and other drugs. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1953 Jun;108(2):129–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greengrass P., Bremner R. Binding characteristics of 3H-prazosin to rat brain alpha-adrenergic receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1979 May 1;55(3):323–326. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(79)90202-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton C. A., Reid J. L., Sumner D. J. Acute effects of phenoxybenzamine on alpha-adrenoceptor responses in vivo and in vitro: relation of in vivo pressor responses to the number of specific adrenoceptor binding sites. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1983 Sep-Oct;5(5):868–873. doi: 10.1097/00005344-198309000-00025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammer R., Kobinger W., Pichler L. Binding of an imidazolidine (clonidine), an oxazoloazepin (B-HT 933) and a thiazoloazepin (B-HT 920) to rat brain alpha-adrenoceptors and relation to cardiovascular effects. Eur J Pharmacol. 1980 Apr 4;62(4):277–285. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(80)90095-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilliard C. C., Bagwell E. E., Daniell H. B. Effects of sympathetic and central nervous system alterations on the blood pressure responses to phentolamine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1972 Mar;180(3):743–747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karliner J. S., Barnes P., Hamilton C. A., Dollery C. T. alpha 1-Adrenergic receptors in guinea pig myocardium: identification by binding of a new radioligand, (3H)-prazosin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Sep 12;90(1):142–149. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91601-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobinger W., Pichler L. Investigation into different types of post- and presynaptic alpha-adrenoceptors at cardiovascular sites in rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1980 Aug 8;65(4):393–402. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(80)90343-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korner P. I., Shaw J., Uther J. B., West M. J., McRitchie R. J., Richards J. G. Autonomic and non-autonomic circulatory components in essential hypertension in man. Circulation. 1973 Jul;48(1):107–117. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.48.1.107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korner P. I. The effect of section of the carotid sinus and aortic nerves on the cardiac output of the rabbit. J Physiol. 1965 Sep;180(2):266–278. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korner P. I., Uther J. B., White S. W. Circulatory effects of chloralose-urethane and sodium pentobarbitone anaesthesis in the rabbit. J Physiol. 1968 Dec;199(2):253–265. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrath J. C. Evidence for more than one type of post-junctional alpha-adrenoceptor. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 Feb 15;31(4):467–484. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90147-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merritt J. C., Olsen J. L., Armstrong J. R., McKinnon S. M. Topical delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol in hypertensive glaucomas. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1981 Jan;33(1):40–41. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1981.tb13699.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid J. L. Acute and chronic beta-receptor blockage with propranolol and the cardiovascular responses to intravenous sodium nitroprusside in the conscious rabbit. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1979 Jul-Aug;1(4):403–414. doi: 10.1097/00005344-197907000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin P. C., Brunton J., Meredith P. Determination of the vasodilator UK33274 by high-performance liquid chromatography using fluorescence detection. J Chromatogr. 1980 Nov 14;221(1):193–195. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)81025-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singleton W., Saxton C. A., Hernandez J., Prichard B. N. Postjunctional selectivity of alpha-blockade with prazosin, trimazosin, and UK-33,274 in man. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1982;4 (Suppl 1):S145–S151. doi: 10.1097/00005344-198200041-00029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens M. J., Moulds R. F. Heterogeneity of post-junctional alpha-adrenoceptors in human vascular smooth muscle. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1981 Nov;254(1):43–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumner D. J., Elliott H. L., Reid J. L. Analysis of the pressor dose response. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1982 Oct;32(4):450–458. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1982.188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmermans P. B., Kwa H. Y., Ali F. K., van Zwieten P. A. Prazosin and its analogues UK-18,596 and UK-33,274: a comparative study on cardiovascular effects and alpha-adrenoceptor blocking activities. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1980 Jun;245(2):218–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmermans P. B., Kwa H. Y., van Zwieten P. A. Possible subdivision of postsynaptic alpha-adrenoceptors mediating pressor responses in the pithed rat. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1979 Dec;310(2):189–193. doi: 10.1007/BF00500284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- U'Prichard D. C., Snyder S. H. Distinct alpha-noradrenergic receptors differentiated by binding and physiological relationships. Life Sci. 1979 Jan 1;24(1):79–88. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(79)90283-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent J., Elliott H. L., Meredith P. A., Reid J. L. Doxazosin, an alpha 1-adrenoceptor antagonist: pharmacokinetics and concentration-effect relationships in man. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1983 Jun;15(6):719–725. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1983.tb01556.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West M. J., Angus J. A., Korner P. I. Estimation of non-autonomic and autonomic components of iliac bed vascular resistance in renal hypertensive rabbits. Cardiovasc Res. 1975 Sep;9(5):697–706. doi: 10.1093/cvr/9.5.697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikberg J. Differentiation between pre- and postjunctional alpha-receptors in guinea pig ileum and rabbit aorta. Acta Physiol Scand. 1978 Jul;103(3):225–239. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1978.tb06210.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yee Y. G., Rubin P. C., Meffin P. Prazosin determination by high-pressure liquid chromatography using fluorescence detection. J Chromatogr. 1979 Apr 21;172:313–318. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)90967-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


