Abstract
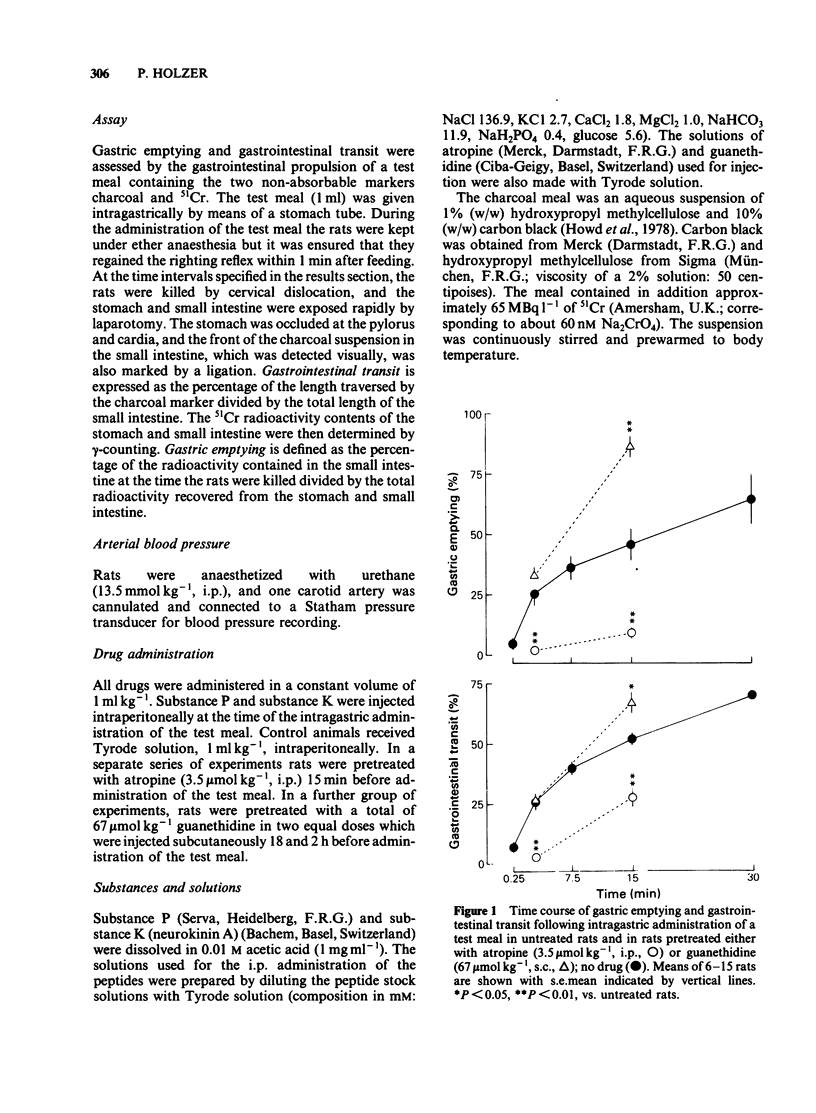
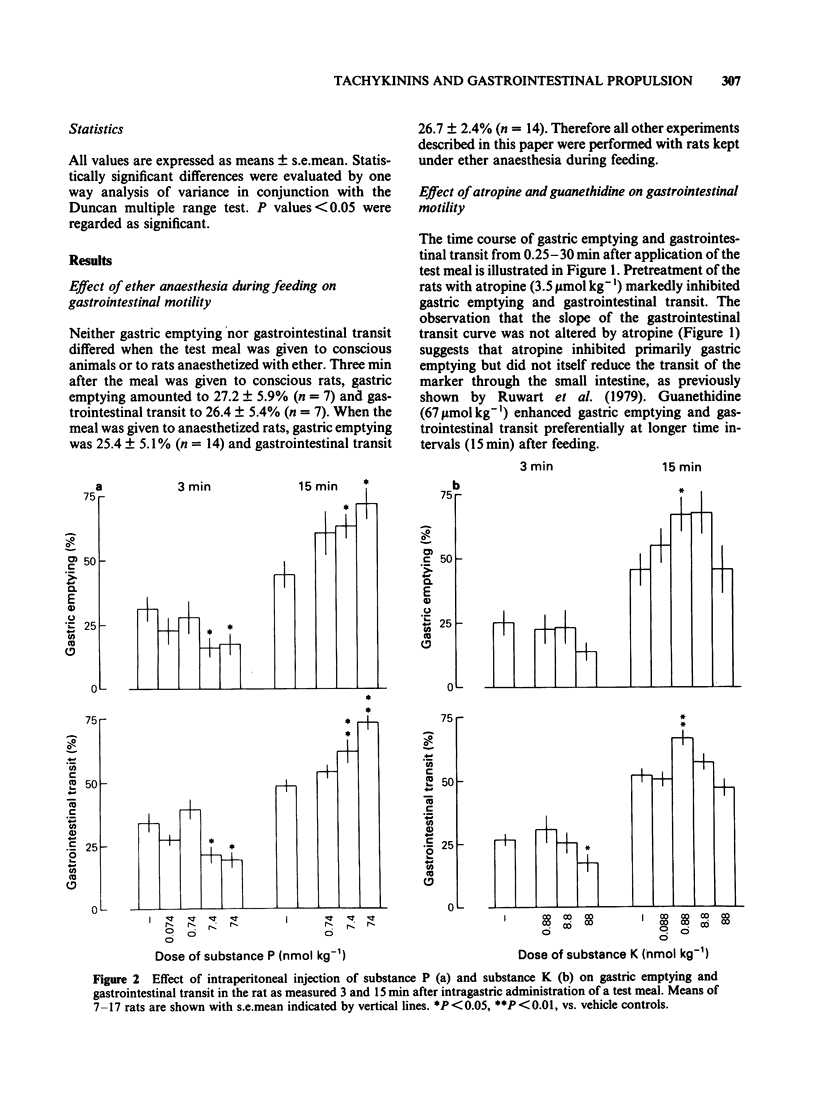
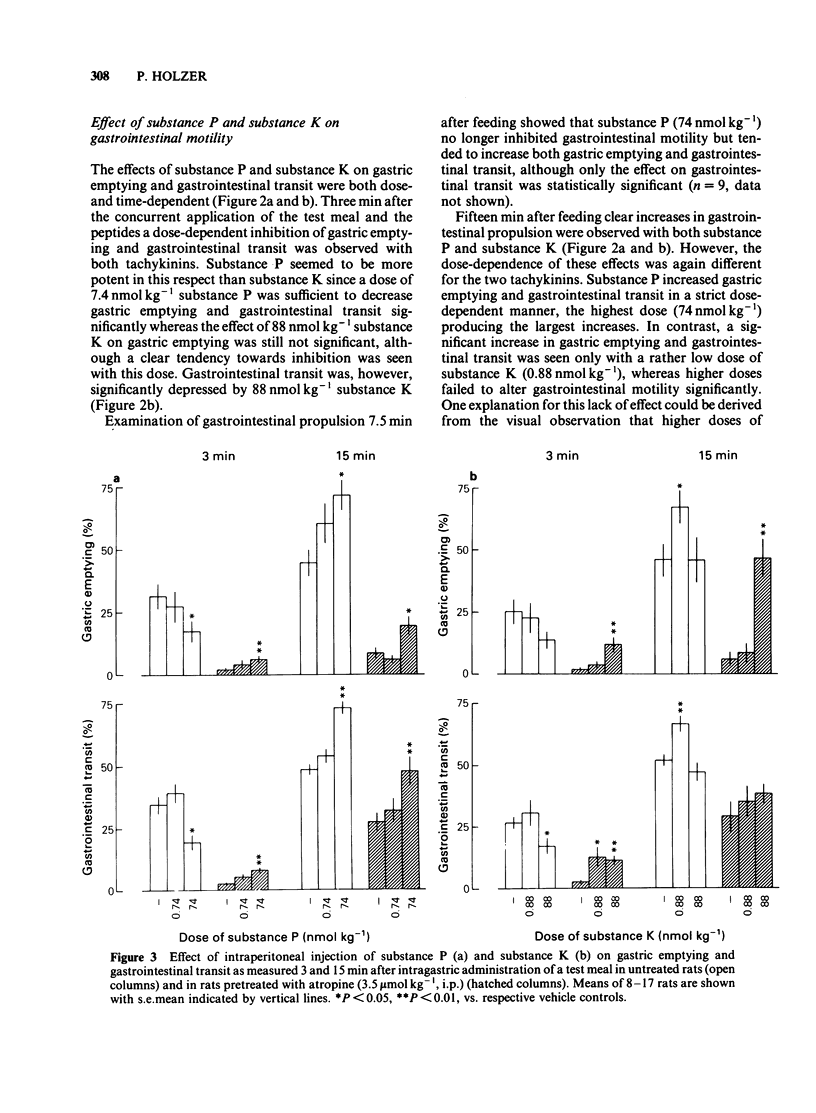
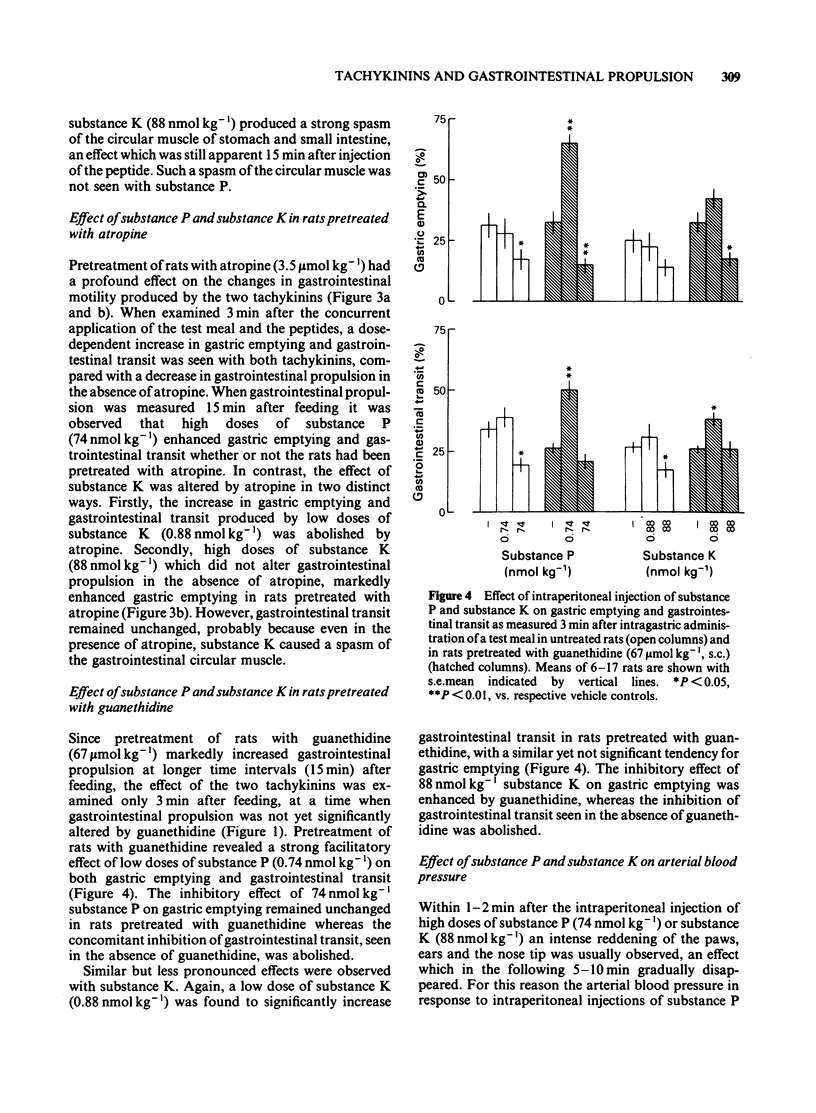
Substance P and substance K (neurokinin A) (dose range: 0.08-80 nmol kg-1) were tested for their effects on gastrointestinal propulsion in the rat. The peptides were given by intraperitoneal injection concurrently with the intragastric administration of a test meal containing charcoal and 51Cr. Examination 3 min after the test meal showed that high doses of substance P (greater than 0.74 nmol kg-1) and substance K (greater than 8.8 nmol kg-1) inhibited gastric emptying and gastrointestinal transit. This inhibitory effect was changed to a stimulant effect by pretreatment of the rats with atropine (3.5 mumol kg-1). Guanethidine pretreatment (67 mumol kg-1) revealed a facilitatory effect of low doses of the two tachykinins (about 1 nmol kg-1) on gastrointestinal propulsion. Examination 15 min after the test meal demonstrated that substance P (greater than 0.74 nmol kg-1) dose-dependently enhanced gastrointestinal propulsion, an effect that was also seen after atropine pretreatment. Low doses of substance K (about 1 nmol kg-1) also stimulated gastrointestinal propulsion but this effect was abolished by atropine. In addition, atropine pretreatment revealed a stimulant effect of high doses of substance K (88 nmol kg-1) on gastric emptying. These results show that the effects of substance P and substance K on gastrointestinal propulsion vary with dose and time and involve, at least partly, activation of the autonomic nervous system.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barthó L., Holzer P., Donnerer J., Lembeck F. Evidence for the involvement of substance P in the atropine-resistant peristalsis of the guinea-pig ileum. Neurosci Lett. 1982 Sep 20;32(1):69–74. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(82)90231-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertaccini G., Coruzzi G. Action of some natural peptides on the stomach of the anaesthetized rat. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1977 Jun;298(2):163–166. doi: 10.1007/BF00508624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertaccini G., de Castiglione R., Scarpignato C. Effect of substance P and its natural analogues on gastric emptying of the conscious rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1981 Feb;72(2):221–223. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1981.tb09116.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa M., Furness J. B., Pullin C. O., Bornstein J. Substance P enteric neurons mediate non-cholinergic transmission to the circular muscle of the guinea-pig intestine. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1985 Feb;328(4):446–453. doi: 10.1007/BF00692914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edin R., Lundberg J. M., Lidberg P., Dahlström A., Ahlman H. Atropine sensitive contractile motor effects of substance P on the feline pylorus and stomach in vivo. Acta Physiol Scand. 1980 Oct;110(2):207–209. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1980.tb06653.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howd R. A., Adamovics A., Palekar A. Naloxone and intestinal motility. Experientia. 1978 Oct 15;34(10):1310–1311. doi: 10.1007/BF01981437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lembeck F., Holzer P., Schweditsch M., Gamse R. Elimination of substance P from the circulation of the rat and its inhibition by bacitracin. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1978 Oct;305(1):9–16. doi: 10.1007/BF00497000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lidberg P., Dahlström A., Lundberg J. M., Ahlman H. Different modes of action of substance P in the motor control of the feline stomach and pylorus. Regul Pept. 1983 Sep;7(1):41–52. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(83)90280-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggio J. E., Hunter J. C. Regional distribution of kassinin-like immunoreactivity in rat central and peripheral tissues and the effect of capsaicin. Brain Res. 1984 Jul 30;307(1-2):370–373. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90498-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangel A. W., Koegel A. Effects of peptides on gastric emptying. Am J Physiol. 1984 Apr;246(4 Pt 1):G342–G345. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1984.246.4.G342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawa H., Doteuchi M., Igano K., Inouye K., Nakanishi S. Substance K: a novel mammalian tachykinin that differs from substance P in its pharmacological profile. Life Sci. 1984 Mar 19;34(12):1153–1160. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(84)90087-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawa H., Hirose T., Takashima H., Inayama S., Nakanishi S. Nucleotide sequences of cloned cDNAs for two types of bovine brain substance P precursor. Nature. 1983 Nov 3;306(5938):32–36. doi: 10.1038/306032a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruwart M. J., Klepper M. S., Rush B. D. Evidence for noncholinergic mediation of small intestinal transit in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1979 Jun;209(3):462–465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theodorsson-Norheim E., Brodin E., Norheim I., Rosell S. Antisera raised against eledoisin and kassinin detect immunoreactive material in rat tissue extracts: tissue distribution and chromatographic characterization. Regul Pept. 1984 Nov;9(4):229–244. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(84)90075-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokoyama S., North R. A. Electrical activity of longitudinal and circular muscle during peristalsis. Am J Physiol. 1983 Jan;244(1):G83–G88. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1983.244.1.G83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


