Abstract
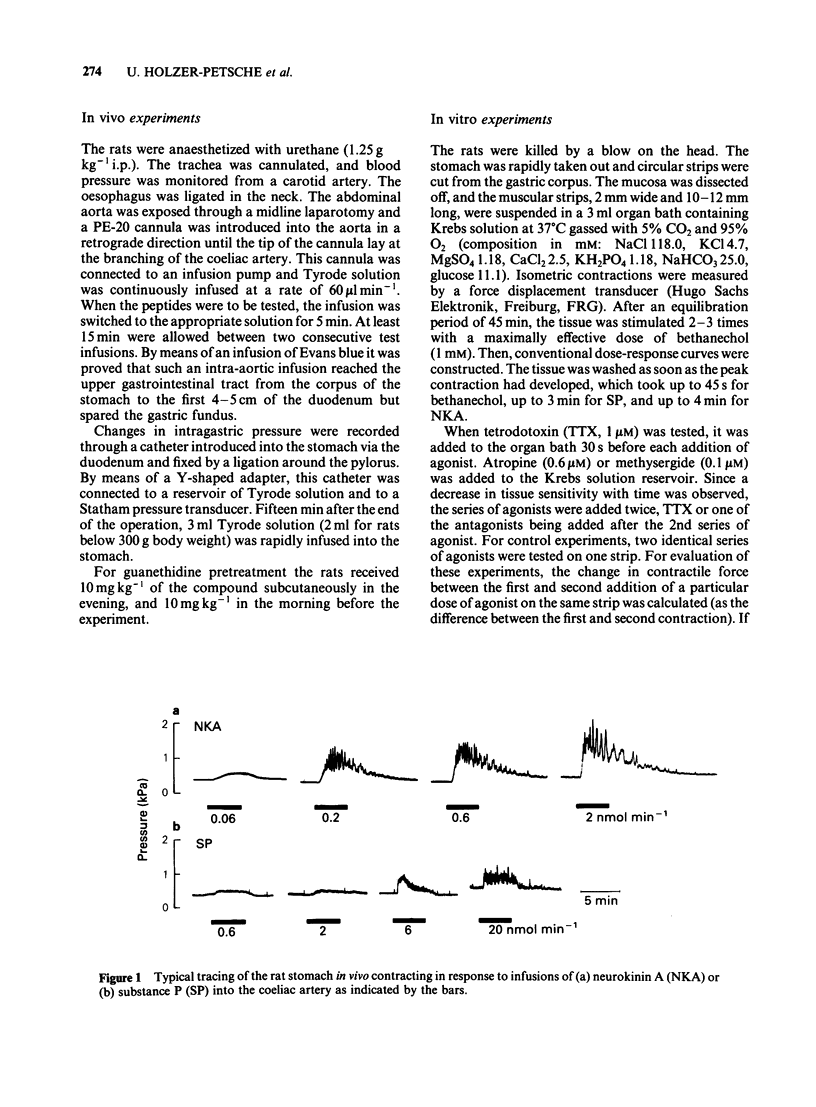
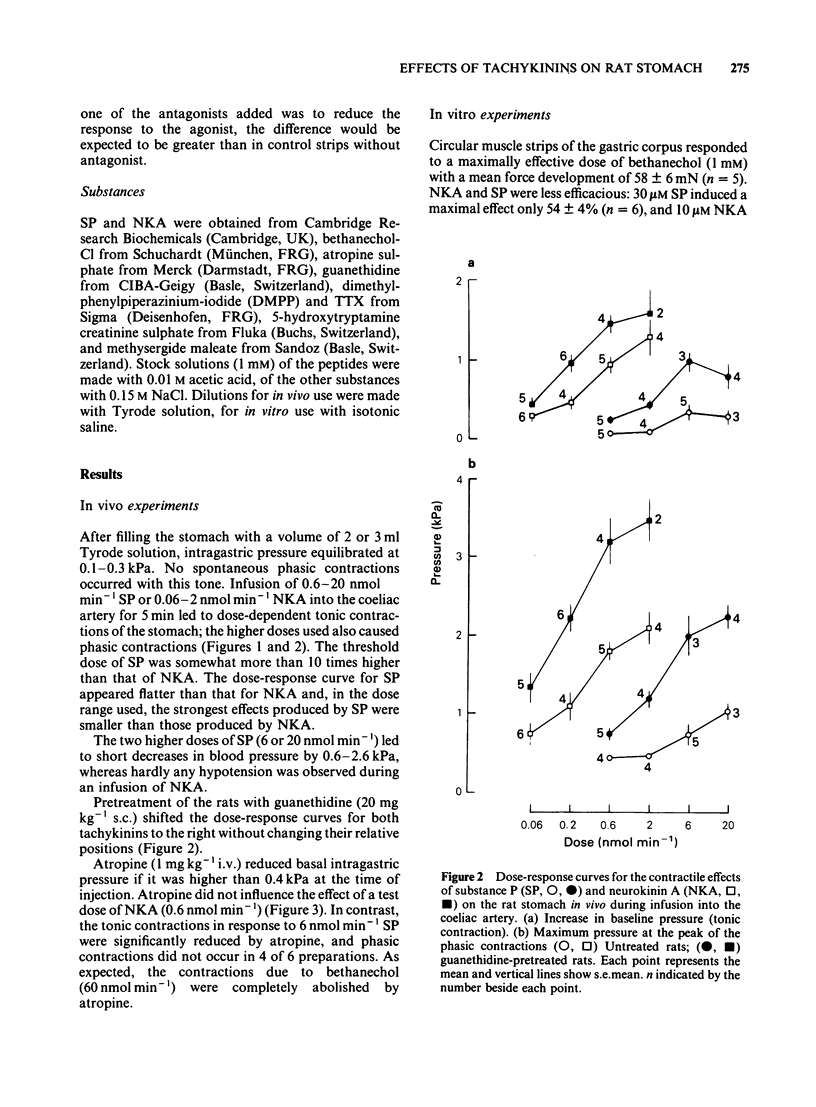
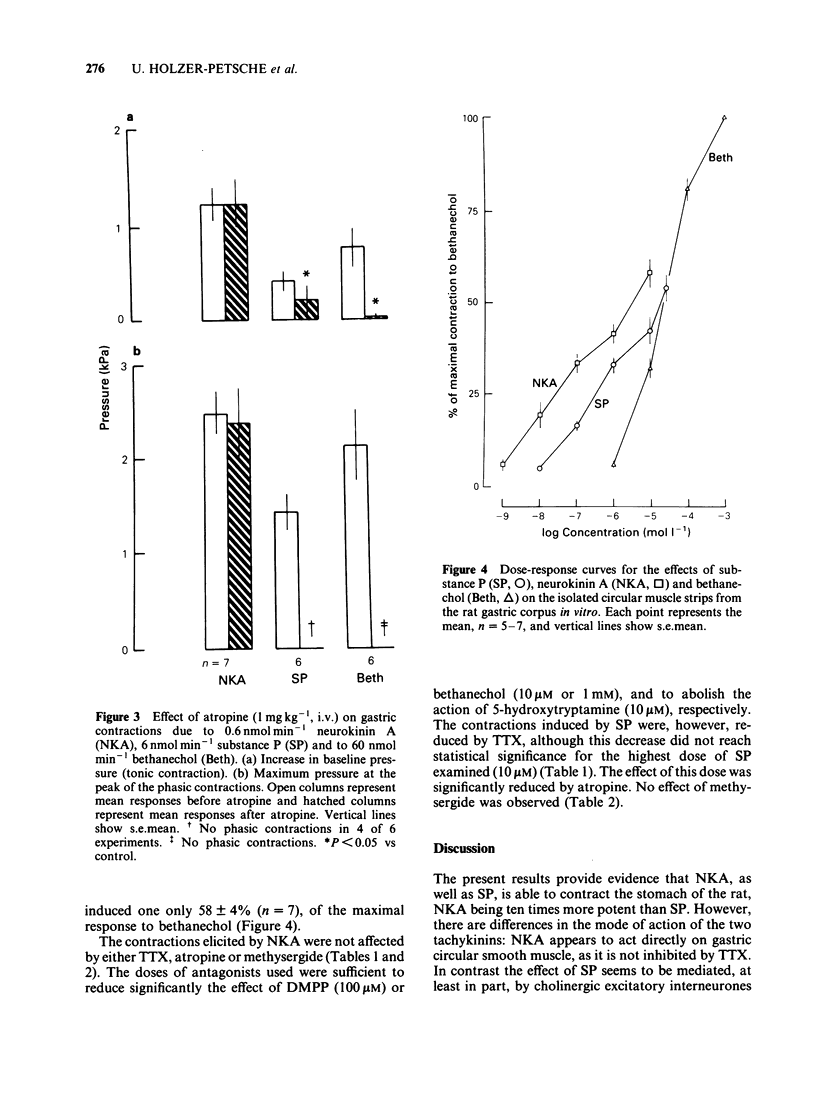
Substance P and neurokinin A (substance K) were infused into the coeliac artery of anaesthetized rats at doses of 0.06-20 nmol min-1. Both tachykinins caused contractions of the stomach, the threshold dose of neurokinin A being 10 times lower than of substance P. The dose-response curve for substance P was flatter than that for neurokinin A. On circular muscle strips from the rat gastric corpus in vitro, the dose-response curves for both tachykinins were parallel, neurokinin A being 10 times more potent than substance P. The contractions in response to 10 microM neurokinin A and to 30 microM substance P were 58 and 54%, respectively, of the maximal contraction to bethanechol (1 mM). The effect of substance P was reduced by atropine both in vivo and in vitro. In vitro, the contractions to substance P were also reduced by tetrodotoxin but left unaffected by methysergide. The action of neurokinin A was not affected by these drugs. It is concluded that neurokinin A contracts rat stomach by a direct action on the circular smooth muscle, whereas the action of substance P is mediated, at least in part, by cholinergic interneurones.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bertaccini G., Coruzzi G. Action of some natural peptides on the stomach of the anaesthetized rat. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1977 Jun;298(2):163–166. doi: 10.1007/BF00508624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burcher E., Buck S. H., Lovenberg W., O'Donohue T. L. Characterization and autoradiographic localization of multiple tachykinin binding sites in gastrointestinal tract and bladder. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Mar;236(3):819–831. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chubb I. W., Hodgson A. J., White G. H. Acetylcholinesterase hydrolyzes substance P. Neuroscience. 1980;5(12):2065–2072. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(80)90124-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edin R., Lundberg J. M., Lidberg P., Dahlström A., Ahlman H. Atropine sensitive contractile motor effects of substance P on the feline pylorus and stomach in vivo. Acta Physiol Scand. 1980 Oct;110(2):207–209. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1980.tb06653.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekblad E., Ekelund M., Graffner H., Håkanson R., Sundler F. Peptide-containing nerve fibers in the stomach wall of rat and mouse. Gastroenterology. 1985 Jul;89(1):73–85. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(85)90747-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. E., Daniel E. E., Jury J., Fox A. E., Collins S. M. Sites and mechanisms of action of neuropeptides on canine gastric motility differ in vivo and in vitro. Life Sci. 1983 Aug 29;33(9):817–825. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(83)90619-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furness J. B., Costa M. Adynamic ileus, its pathogenesis and treatment. Med Biol. 1974 Apr;52(2):82–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzer P. Stimulation and inhibition of gastrointestinal propulsion induced by substance P and substance K in the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Sep;86(1):305–312. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb09462.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew W. Y., Longhurst J. C. Substance P, 5-hydroxytryptamine, and bradykinin stimulate abdominal visceral afferents. Am J Physiol. 1986 Mar;250(3 Pt 2):R465–R473. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1986.250.3.R465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lidberg P., Dahlström A., Ahlman H. On the nature of the contractile motor responses of the rat stomach elicited by serotonin or substance P in vitro. J Neural Transm. 1985;63(1):73–89. doi: 10.1007/BF01249585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milenov K., Golenhofen K. Differentiated contractile responses of gastric smooth muscle to substance P. Pflugers Arch. 1983 Apr;397(1):29–34. doi: 10.1007/BF00585164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milenov K., Nieber K., Oehme P. A selective tonic activation of gastrointestinal smooth muscle by substance P. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1978 Oct;235(2):219–229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minagawa H., Shiosaka S., Inoue H., Hayashi N., Kasahara A., Kamata T., Tohyama M., Shiotani Y. Origins and three-dimensional distribution of substance P-containing structures on the rat stomach using whole-mount tissue. Gastroenterology. 1984 Jan;86(1):51–59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawa H., Doteuchi M., Igano K., Inouye K., Nakanishi S. Substance K: a novel mammalian tachykinin that differs from substance P in its pharmacological profile. Life Sci. 1984 Mar 19;34(12):1153–1160. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(84)90087-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawa H., Kotani H., Nakanishi S. Tissue-specific generation of two preprotachykinin mRNAs from one gene by alternative RNA splicing. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):729–734. doi: 10.1038/312729a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultzberg M., Hökfelt T., Nilsson G., Terenius L., Rehfeld J. F., Brown M., Elde R., Goldstein M., Said S. Distribution of peptide- and catecholamine-containing neurons in the gastro-intestinal tract of rat and guinea-pig: immunohistochemical studies with antisera to substance P, vasoactive intestinal polypeptide, enkephalins, somatostatin, gastrin/cholecystokinin, neurotensin and dopamine beta-hydroxylase. Neuroscience. 1980;5(4):689–744. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(80)90166-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharkey K. A., Williams R. G., Dockray G. J. Sensory substance P innervation of the stomach and pancreas. Demonstration of capsaicin-sensitive sensory neurons in the rat by combined immunohistochemistry and retrograde tracing. Gastroenterology. 1984 Oct;87(4):914–921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theodorsson-Norheim E., Brodin E., Norheim I., Rosell S. Antisera raised against eledoisin and kassinin detect immunoreactive material in rat tissue extracts: tissue distribution and chromatographic characterization. Regul Pept. 1984 Nov;9(4):229–244. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(84)90075-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Nueten J. M., Leysen J. E., de Clerck F., Vanhoutte P. M. Serotonergic receptor subtypes and vascular reactivity. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1984;6 (Suppl 4):S564–S574. doi: 10.1097/00005344-198406004-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


