Abstract
1. We describe the actions of GR43175, a 5-hydroxytryptamine1 (5-HT1)-like receptor agonist, on neurogenically-mediated plasma protein extravasation within an important pain-sensitive intracranial tissue, the dura mater. 2. GR43175 markedly attenuated extravasation of 125I-albumin from blood vessels within ipsilateral dura mater when administered to rats (100 micrograms kg-1) fifteen minutes before unilateral electrical trigeminal stimulation (1.2 mA, 5 Hz, 5 ms, 5 min); the ratio (stimulated/unstimulated sides) decreased from 1.81 to 1.23, P less than 0.005). 3. GR43175 (100 micrograms kg-1, i.v., rats; 30 micrograms kg-1, guinea-pigs) decreased the leakage of radiolabelled albumin from 163% to 119% (P less than 0.005, guinea-pig) or from 174 to 118% (P less than 0.05, rat) above vehicle-treated controls when injected ten minutes before systemic capsaicin treatment (0.5 or 1 mumol kg-1, i.v.). 4. GR43175 (30-300 micrograms kg-1) did not block plasma protein extravasation within extracranial tissues of rats and guinea-pigs innervated by the trigeminal nerve (conjunctiva, eyelid and lip). 5. The protein leakage which followed the i.v. administration of 5-HT (1 mumol kg-1) or neuropeptides which mediate neurogenic plasma extravasation, substance P (0.3 nmol kg-1 or 1 nmol kg-1) and neurokinin A (1 nmol kg-1), was not blocked by GR43175 (100, 300 micrograms kg-1) despite the presence of leakage in amounts equivalent to that following neurogenic stimulation. 6. GR43175 (100 micrograms kg-1) decreased bradykinin (10 mumol kg-1)-induced extravasation from 142 to 115% above vehicle-treated animals (P less than 0.05).(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF
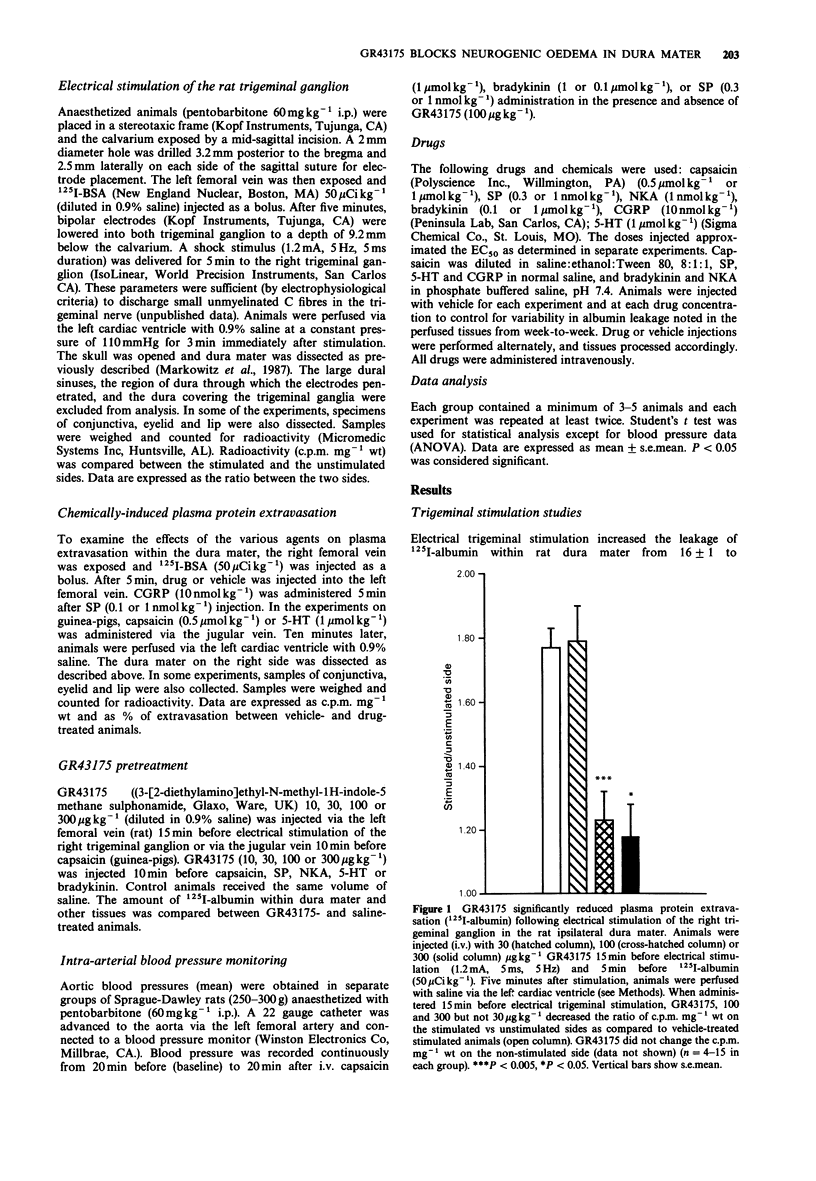
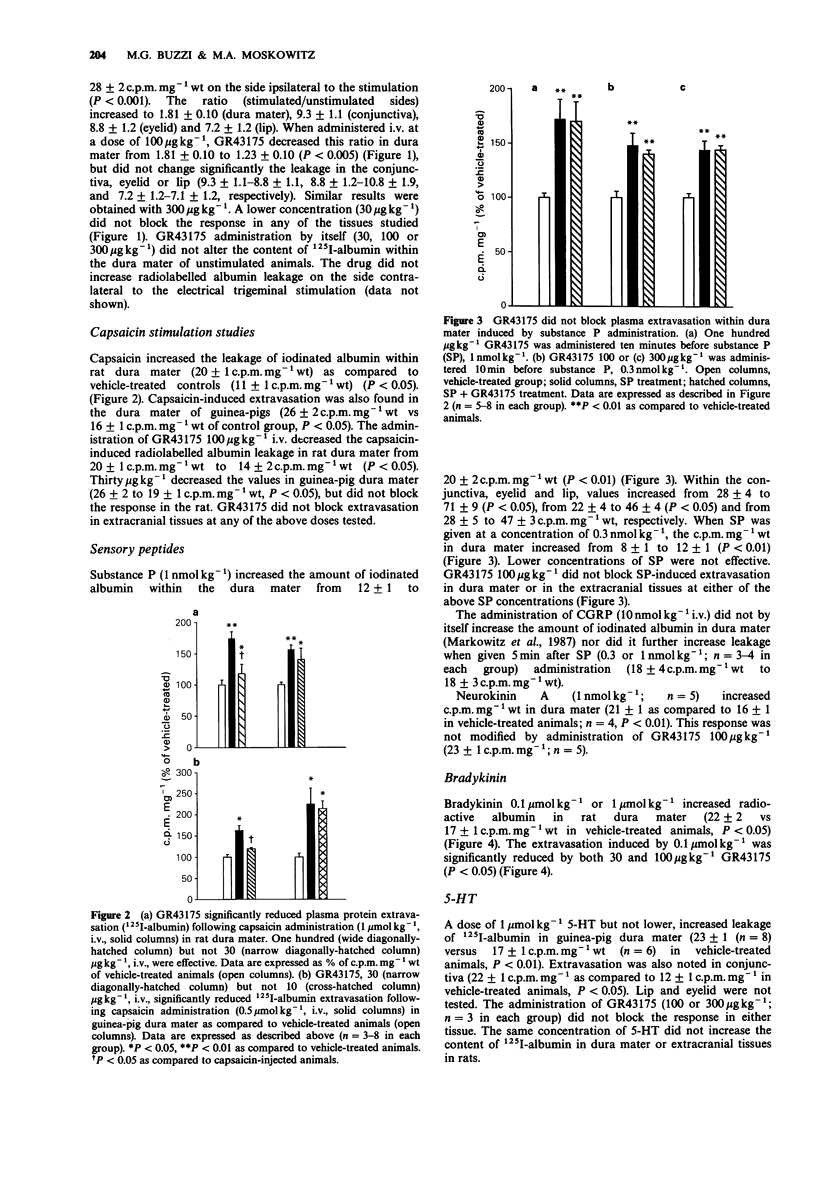
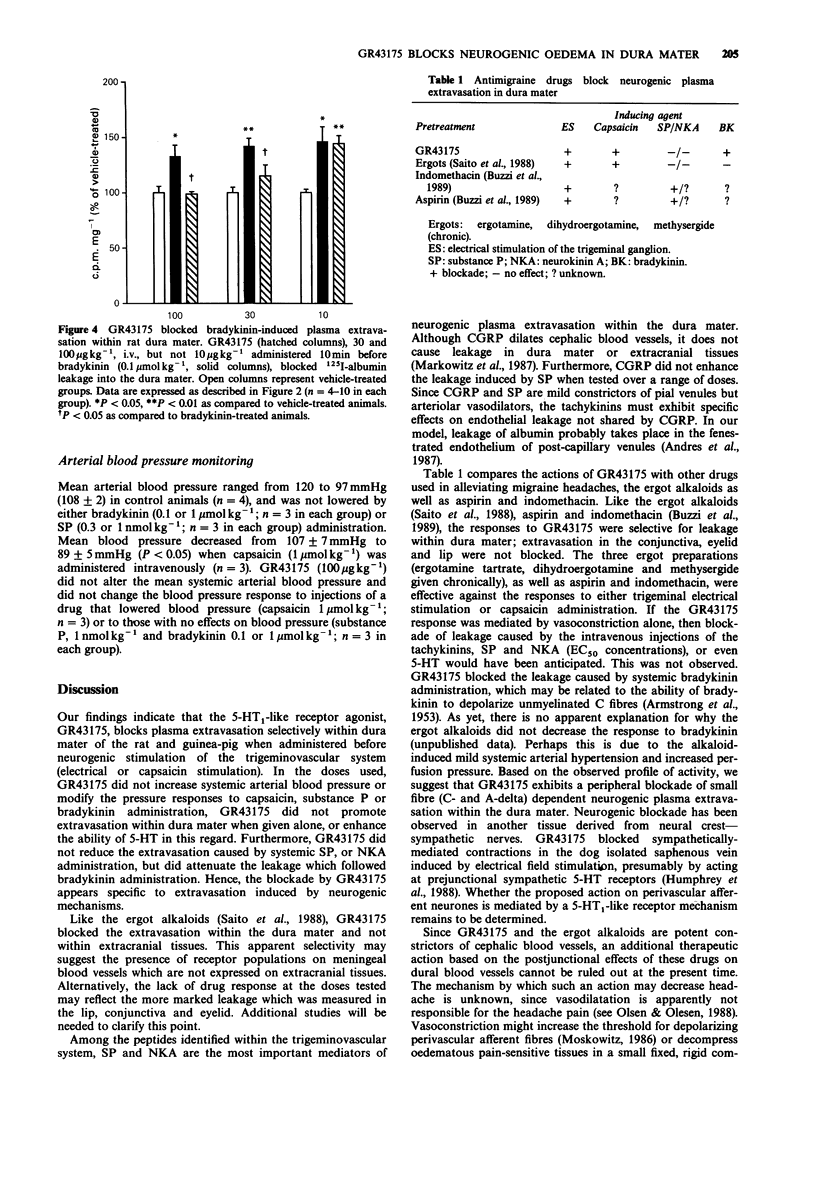

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARMSTRONG D., DRY R. M. L., KEELE C. A., MARKHAM J. W. Observations on chemical excitants of cutaneous pain in man. J Physiol. 1953 May 28;120(3):326–351. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ala-Hurula V., Myllylä V. V., Arvela P., Kärki N. T., Hokkanen E. Systemic availability of ergotamine tartrate after three successive doses and during continuous medication. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1979 Nov;16(5):355–360. doi: 10.1007/BF00605636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andres K. H., von Düring M., Muszynski K., Schmidt R. F. Nerve fibres and their terminals of the dura mater encephali of the rat. Anat Embryol (Berl) 1987;175(3):289–301. doi: 10.1007/BF00309843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brain S. D., Williams T. J., Tippins J. R., Morris H. R., MacIntyre I. Calcitonin gene-related peptide is a potent vasodilator. Nature. 1985 Jan 3;313(5997):54–56. doi: 10.1038/313054a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buzzi M. G., Sakas D. E., Moskowitz M. A. Indomethacin and acetylsalicylic acid block neurogenic plasma protein extravasation in rat dura mater. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Jun 20;165(2-3):251–258. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90719-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doenicke A., Brand J., Perrin V. L. Possible benefit of GR43175, a novel 5-HT1-like receptor agonist, for the acute treatment of severe migraine. Lancet. 1988 Jun 11;1(8598):1309–1311. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)92122-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edvinsson L., Uddman R. Immunohistochemical localization and dilatatory effect of substance P on human cerebral vessels. Brain Res. 1982 Jan 28;232(2):466–471. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90290-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardebo J. E. The involvement of trigeminal substance P neurons in cluster headache. An hypothesis. Headache. 1984 Nov;24(6):294–304. doi: 10.1111/j.1526-4610.1984.hed2406294.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey P. P., Feniuk W., Perren M. J., Connor H. E., Oxford A. W., Coates L. H., Butina D. GR43175, a selective agonist for the 5-HT1-like receptor in dog isolated saphenous vein. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Aug;94(4):1123–1132. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11630.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen I., Uddman R., Hocherman M., Ekman R., Jensen K., Olesen J., Stiernholm P., Edvinsson L. Localization and effects of neuropeptide Y, vasoactive intestinal polypeptide, substance P, and calcitonin gene-related peptide in human temporal arteries. Ann Neurol. 1986 Oct;20(4):496–501. doi: 10.1002/ana.410200409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lembeck F., Holzer P. Substance P as neurogenic mediator of antidromic vasodilation and neurogenic plasma extravasation. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1979 Dec;310(2):175–183. doi: 10.1007/BF00500282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markowitz S., Saito K., Moskowitz M. A. Neurogenically mediated leakage of plasma protein occurs from blood vessels in dura mater but not brain. J Neurosci. 1987 Dec;7(12):4129–4136. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-12-04129.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayberg M. R., Zervas N. T., Moskowitz M. A. Trigeminal projections to supratentorial pial and dural blood vessels in cats demonstrated by horseradish peroxidase histochemistry. J Comp Neurol. 1984 Feb 10;223(1):46–56. doi: 10.1002/cne.902230105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayberg M., Langer R. S., Zervas N. T., Moskowitz M. A. Perivascular meningeal projections from cat trigeminal ganglia: possible pathway for vascular headaches in man. Science. 1981 Jul 10;213(4504):228–230. doi: 10.1126/science.6166046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moskowitz M. A., Reinhard J. F., Jr, Romero J., Melamed E., Pettibone D. J. Neurotransmitters and the fifth cranial nerve: is there a relation to the headache phase of migraine? Lancet. 1979 Oct 27;2(8148):883–885. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)92692-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moskowitz M. A. The neurobiology of vascular head pain. Ann Neurol. 1984 Aug;16(2):157–168. doi: 10.1002/ana.410160202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito K., Greenberg S., Moskowitz M. A. Trigeminal origin of beta-preprotachykinin products in feline pial blood vessels. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Apr 23;76(1):69–73. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90194-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito K., Markowitz S., Moskowitz M. A. Ergot alkaloids block neurogenic extravasation in dura mater: proposed action in vascular headaches. Ann Neurol. 1988 Dec;24(6):732–737. doi: 10.1002/ana.410240607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saria A., Gamse R., Petermann J., Fischer J. A., Theodorsson-Norheim E., Lundberg J. M. Simultaneous release of several tachykinins and calcitonin gene-related peptide from rat spinal cord slices. Neurosci Lett. 1986 Jan 30;63(3):310–314. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(86)90376-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


