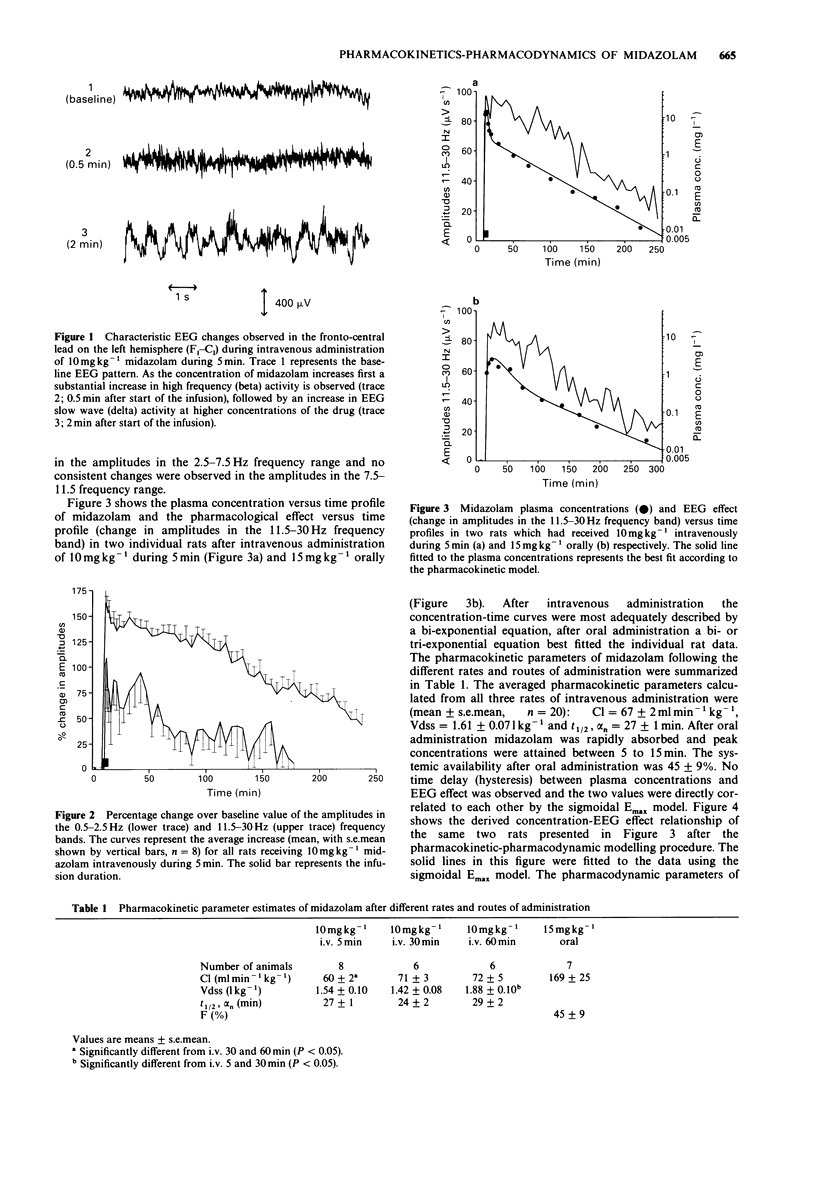
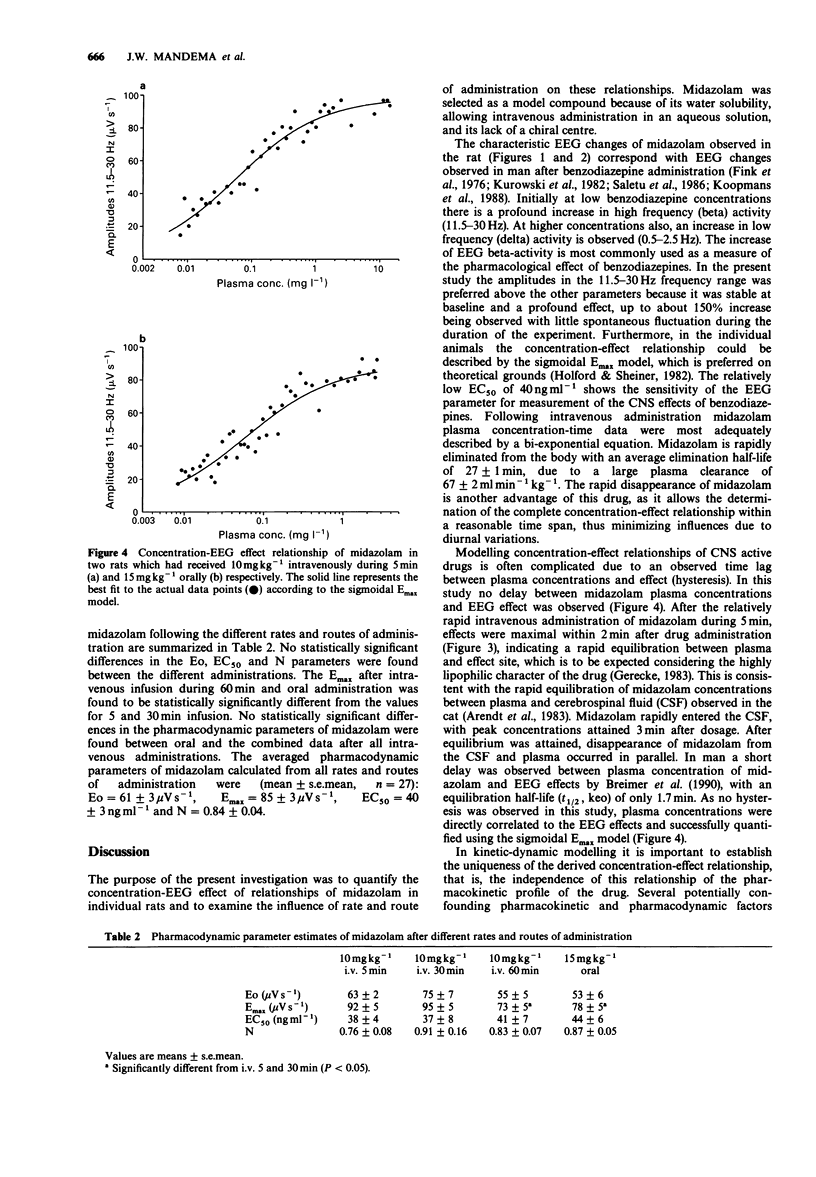
Abstract
1. The purpose of the present investigation was to quantify the concentration-pharmacological effect relationship of midazolam in individual rats by use of effect parameters derived from aperiodic EEG analysis. By varying the rate and route of administration the role of (inter)active metabolites and development of acute tolerance was evaluated. 2. The pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of midazolam were determined after intravenous administration of 10 mg kg-1 during 5, 30 and 60 min and oral administration of 15 mg kg-1. Following intravenous administration the pharmacokinetics were most adequately described by a bi-exponential equation. The values (mean +/- s.e. mean, n = 20) of clearance, volume of distribution at steady-state and terminal half-life were 67 +/- 2 ml min-1 kg-1, 1.61 +/- 0.071 kg-1 and 27 +/- 1 min, respectively. Following oral administration midazolam was rapidly absorbed with a systemic availability of 45 +/- 9%. 3. The averaged amplitudes in the 11.5-30 Hz (beta) frequency band of the fronto-central lead on the left-hemisphere, as derived by aperiodic EEG analysis, was selected as a measure of the pharmacological effect of midazolam. By pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic modelling the individual concentration-EEG effect relationships of midazolam were derived, which were successfully quantified by the sigmoidal Emax model. No marked and systematic differences in pharmacodynamic parameters were found between the rates and routes of administration.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arendt R. M., Greenblatt D. J., deJong R. H., Bonin J. D., Abernethy D. R., Ehrenberg B. L., Giles H. G., Sellers E. M., Shader R. I. In vitro correlates of benzodiazepine cerebrospinal fluid uptake, pharmacodynamic action and peripheral distribution. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Oct;227(1):98–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breimer L. T., Hennis P. J., Burm A. G., Danhof M., Bovill J. G., Spierdijk J., Vletter A. A. Quantification of the EEG effect of midazolam by aperiodic analysis in volunteers. Pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic modelling. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1990 Mar;18(3):245–253. doi: 10.2165/00003088-199018030-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crevoisier C., Ziegler W. H., Eckert M., Heizmann P. Relationship between plasma concentration and effect of midazolam after oral and intravenous administration. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1983;16 (Suppl 1):51S–61S. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1983.tb02271.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingemanse J., Danhof M., Breimer D. D. Pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic modeling of CNS drug effects: an overview. Pharmacol Ther. 1988;38(1):1–52. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(88)90101-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingemanse J., Thomassen D., Mentink B. H., Danhof M. Strategy to assess the role of (inter)active metabolites in pharmacodynamic studies in-vivo: a model study with heptabarbital. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1988 Aug;40(8):552–557. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1988.tb05301.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellinwood E. H., Jr, Heatherly D. G., Nikaido A. M., Bjornsson T. D., Kilts C. Comparative pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of lorazepam, alprazolam and diazepam. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1985;86(4):392–399. doi: 10.1007/BF00427897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellinwood E. H., Jr, Linnoila M., Easler M. E., Molter D. W. Profile of acute tolerance to three sedative anxiolytics. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1983;79(2-3):137–141. doi: 10.1007/BF00427800. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- File S. E., Wilks L. J., Mabbutt P. S. Withdrawal, tolerance and sensitization after a single dose of lorazepam. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1988 Dec;31(4):937–940. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(88)90408-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink M., Weinfeld R. E., Schwartz M. A., Conney A. H. Blood levels and electroencephalographic effects of diazepam and bromazepam. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1976 Aug;20(2):184–191. doi: 10.1002/cpt1976202184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenblatt D. J., Ehrenberg B. L., Gunderman J., Locniskar A., Scavone J. M., Harmatz J. S., Shader R. I. Pharmacokinetic and electroencephalographic study of intravenous diazepam, midazolam, and placebo. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1989 Apr;45(4):356–365. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1989.41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenblatt D. J., Shader R. I., Harmatz J. S., Franke K., Koch-Weser J. Absorption rate, blood concentrations, and early response to oral chlordiazepoxide. Am J Psychiatry. 1977 May;134(5):559–562. doi: 10.1176/ajp.134.5.559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregory T. K., Pettus D. C. An electroencephalographic processing algorithm specifically intended for analysis of cerebral electrical activity. J Clin Monit. 1986 Jul;2(3):190–197. doi: 10.1007/BF01620551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundström R., Holmberg G., Hansen T. Degree of sedation obtained with various doses of diazepam and nitrazepam. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1978 Jul;43(1):13–18. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1978.tb02226.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heizmann P., Eckert M., Ziegler W. H. Pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of midazolam in man. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1983;16 (Suppl 1):43S–49S. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1983.tb02270.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holford N. H., Sheiner L. B. Kinetics of pharmacologic response. Pharmacol Ther. 1982;16(2):143–166. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(82)90051-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koopmans R., Dingemanse J., Danhof M., Horsten G. P., van Boxtel C. J. Pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic modeling of midazolam effects on the human central nervous system. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1988 Jul;44(1):14–22. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1988.106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurowski M., Ott H., Herrmann W. M. Relationship between EEG dynamics and pharmacokinetics of the benzodiazepine lormetazepam. Pharmacopsychiatria. 1982 May;15(3):77–83. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1019513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurian S., Gaillard J. M., Le P. K., Schöpf J. Effects of a benzodiazepine antagonist on the diazepam-induced electrical brain activity modifications. Neuropsychobiology. 1984;11(1):55–58. doi: 10.1159/000118052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLeod S. M., Giles H. G., Patzalek G., Thiessen J. J., Sellers E. M. Diazepam actions and plasma concentrations following ethanol ingestion. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1977;11(5):345–349. doi: 10.1007/BF00566531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandema J. W., Danhof M. Pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic modeling of the central nervous system effects of heptabarbital using aperiodic EEG analysis. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1990 Oct;18(5):459–481. doi: 10.1007/BF01061705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieri L., Schaffner R., Scherschlicht R., Polc P., Sepinwall J., Davidson A., Möhler H., Cumin R., Da Prada M., Burkard W. P. Pharmacology of midazolam. Arzneimittelforschung. 1981;31(12A):2180–2201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reves J. G., Fragen R. J., Vinik H. R., Greenblatt D. J. Midazolam: pharmacology and uses. Anesthesiology. 1985 Mar;62(3):310–324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saletu B., Grünberger J., Sieghart W. Pharmaco-EEG, behavioural methods and blood levels in the comparison of temazepam and flunitrazepam. Acta Psychiatr Scand Suppl. 1986;332:67–94. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0447.1986.tb08984.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellers E. M. Addictive drugs: disposition, tolerance, and dependence interrelationships. Drug Metab Rev. 1978;8(1):5–11. doi: 10.3109/03602537808993774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woo G. K., Williams T. H., Kolis S. J., Warinsky D., Sasso G. J., Schwartz M. A. Biotransformation of [14C]midazolam in the rat in vitro and in vivo. Xenobiotica. 1981 Jun;11(6):373–384. doi: 10.3109/00498258109045848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoong Y. L., Lee H. S., Gwee M. C., Wong P. T. Acute tolerance to diazepam in mice: pharmacokinetic considerations. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1986 Feb;13(2):153–158. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.1986.tb00329.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler W. H., Schalch E., Leishman B., Eckert M. Comparison of the effects of intravenously administered midazolam, triazolam and their hydroxy metabolites. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1983;16 (Suppl 1):63S–69S. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1983.tb02272.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


