Abstract
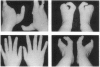
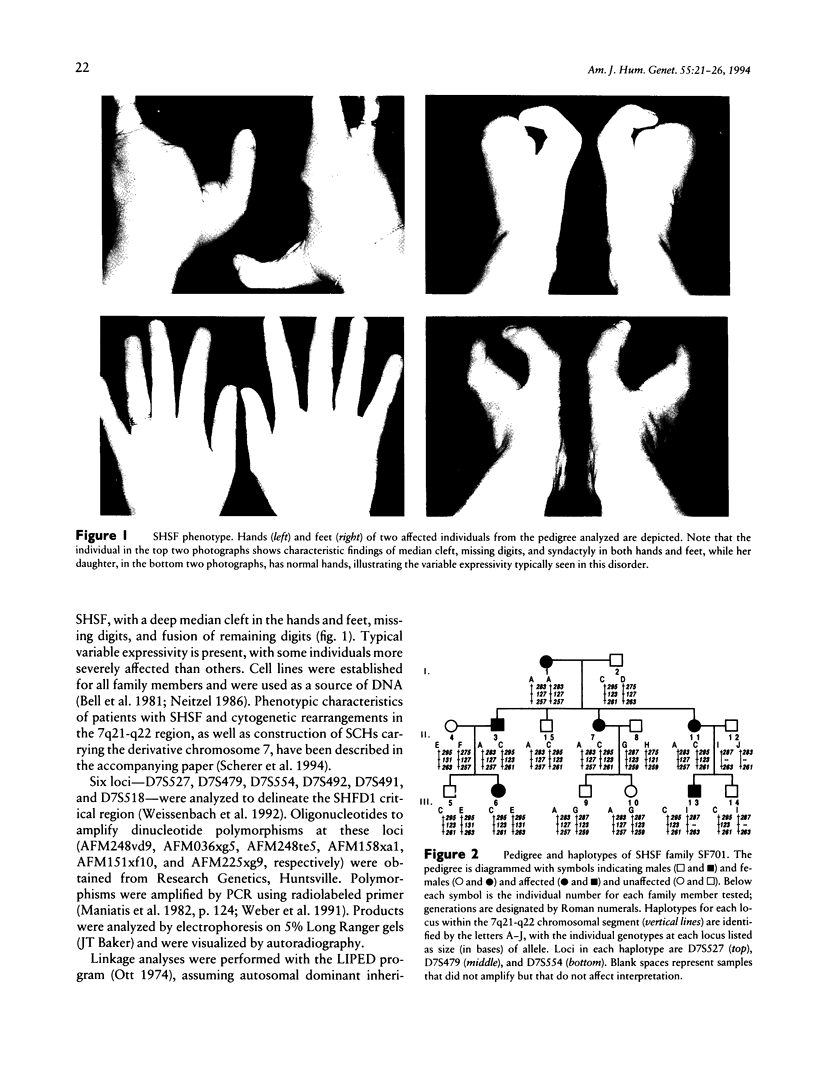
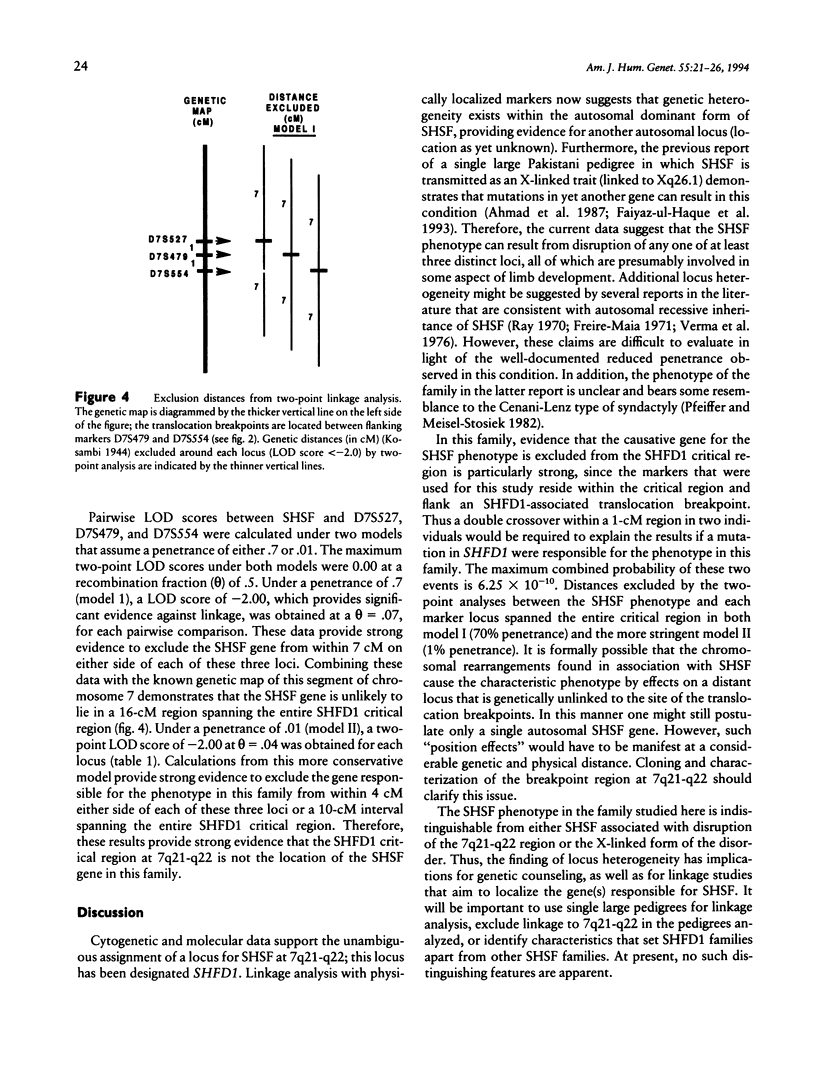
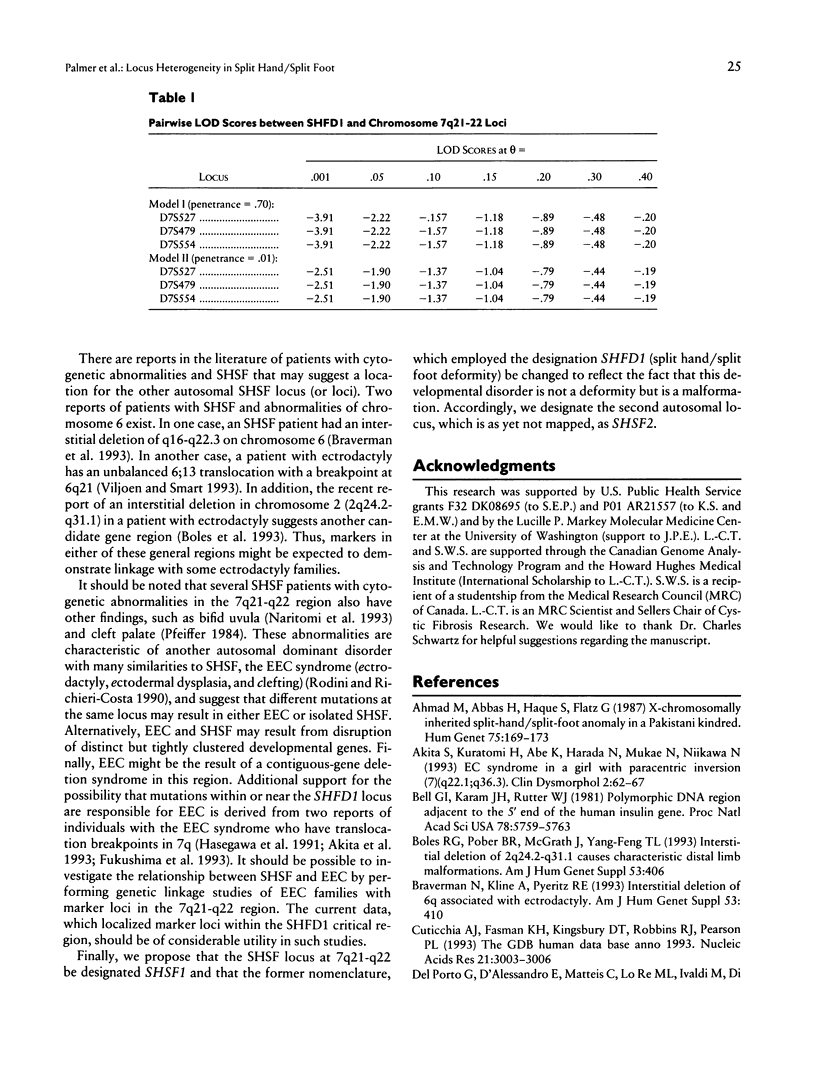
Split hand/split foot (SHSF; also known as ectrodactyly) is a human developmental disorder characterized by missing central digits and other distal limb malformations. An association between SHSF and cytogenetically visible rearrangements of chromosome 7 at bands q21-q22 provides compelling evidence for the location of a causative gene at this location, and the locus has been designated SHFD1. In the present study, marker loci were localized to the SHFD1 critical region through the analysis of somatic cell hybrids derived from individuals with SHSF and cytogenetic abnormalities involving the 7q21-q22 region. Combined genetic and physical data suggest that the order of markers in the SHFD1 critical region is cen-D7S492-D7S527-(D7S479-D7S491)-SHFD1-++ +D7S554-D7S518-qter. Dinucleotide repeat polymorphisms at three of these loci were used to test for linkage of SHSF to this region in a large pedigree that demonstrates autosomal dominant SHSF. Evidence against linkage of the SHSF gene to 7q21-q22 was obtained in this pedigree. Therefore, combined molecular and genetic data provide evidence for locus heterogeneity in autosomal dominant SHSF. We propose the name SHSF2 for this second locus.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmad M., Abbas H., Haque S., Flatz G. X-chromosomally inherited split-hand/split-foot anomaly in a Pakistani kindred. Hum Genet. 1987 Feb;75(2):169–173. doi: 10.1007/BF00591081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akita S., Kuratomi H., Abe K., Harada N., Mukae N., Niikawa N. EC syndrome in a girl with paracentric inversion (7)(q22.1;q36.3). Clin Dysmorphol. 1993 Jan;2(1):62–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell G. I., Karam J. H., Rutter W. J. Polymorphic DNA region adjacent to the 5' end of the human insulin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5759–5763. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuticchia A. J., Fasman K. H., Kingsbury D. T., Robbins R. J., Pearson P. L. The GDB human genome data base anno 1993. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jul 1;21(13):3003–3006. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.13.3003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Porto G., D'Alessandro E., De Matteis C., Lo Re M. L., Ivaldi M., Di Fusco C. Delezione interstiziale del braccio lungo del cromosoma 7 e sue correlazioni cliniche. Pathologica. 1983;75 (Suppl):268–271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faiyaz ul Haque M., Uhlhaas S., Knapp M., Schüler H., Friedl W., Ahmad M., Propping P. Mapping of the gene for X-chromosomal split-hand/split-foot anomaly to Xq26-q26.1. Hum Genet. 1993 Mar;91(1):17–19. doi: 10.1007/BF00230215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freire-Maia A. A recessive form of ectrodactyly, and its implications in genetic counseling. J Hered. 1971 Jan-Feb;62(1):53–53. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jhered.a108124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukushima Y., Ohashi H., Hasegawa T. The breakpoints of the EEC syndrome (ectrodactyly, ectodermal dysplasia and cleft lip/palate) confirmed to 7q11.21 and 9p12 by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Clin Genet. 1993 Jul;44(1):50–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1993.tb03843.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genuardi M., Pomponi M. G., Sammito V., Bellussi A., Zollino M., Neri G. Split hand/split foot anomaly in a family segregating a balanced translocation with breakpoint on 7q22.1. Am J Med Genet. 1993 Nov 1;47(6):823–831. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320470606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa T., Hasegawa Y., Asamura S., Nagai T., Tsuchiya Y., Ninomiya M., Fukushima Y. EEC syndrome (ectrodactyly, ectodermal dysplasia and cleft lip/palate) with a balanced reciprocal translocation between 7q11.21 and 9p12 (or 7p11.2 and 9q12) in three generations. Clin Genet. 1991 Sep;40(3):202–206. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1991.tb03077.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morey M. A., Higgins R. R. Ectro-amelia syndrome associated with an interstitial deletion of 7q. Am J Med Genet. 1990 Jan;35(1):95–99. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320350118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naritomi K., Izumikawa Y., Tohma T., Hirayama K. Inverted insertion of chromosome 7q and ectrodactyly. Am J Med Genet. 1993 Jun 15;46(5):492–493. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320460505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neitzel H. A routine method for the establishment of permanent growing lymphoblastoid cell lines. Hum Genet. 1986 Aug;73(4):320–326. doi: 10.1007/BF00279094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott J. Estimation of the recombination fraction in human pedigrees: efficient computation of the likelihood for human linkage studies. Am J Hum Genet. 1974 Sep;26(5):588–597. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeiffer R. A. Interstitial deletion of a chromosome 7 (q11.2q22.1) in a child with splithand/splitfoot malformation. Ann Genet. 1984;27(1):45–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeiffer R. A., Meisel-Stosiek M. Present nosology of the Cenani-Lenz type of syndactyly. Clin Genet. 1982 Jan;21(1):74–79. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1982.tb02083.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray A. K. Another case of split-foot mutation in two sibs. J Hered. 1970 Jul-Aug;61(4):169–170. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jhered.a108073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivera H., Sanchez-Corona J., Burgos-Fuentes V. R., Melendez-Ruiz M. J. Deletion of 7q22 and ectrodactyly. Genet Couns. 1991;2(1):27–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts S. H., Hughes H. E., Davies S. J., Meredith A. L. Bilateral split hand and split foot malformation in a boy with a de novo interstitial deletion of 7q21.3. J Med Genet. 1991 Jul;28(7):479–481. doi: 10.1136/jmg.28.7.479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodini E. S., Richieri-Costa A. EEC syndrome: report on 20 new patients, clinical and genetic considerations. Am J Med Genet. 1990 Sep;37(1):42–53. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320370112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer S. W., Rommens J. M., Soder S., Wong E., Plavsic N., Tompkins B. J., Beattie A., Kim J., Tsui L. C. Refined localization and yeast artificial chromosome (YAC) contig--mapping of genes and DNA segments in the 7q21-q32 region. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Jun;2(6):751–760. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.6.751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharland M., Patton M. A., Hill L. Ectrodactyly of hands and feet in a child with a complex translocation including 7q21.2. Am J Med Genet. 1991 Jun 15;39(4):413–414. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320390410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tajara E. H., Varella-Garcia M., Gusson A. C. Interstitial long-arm deletion of chromosome 7 and ectrodactyly. Am J Med Genet. 1989 Feb;32(2):192–194. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320320212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma I. C., Joseph R., Bhargava S., Mehta S. Split-hand and split-foot deformity inherited as an autosomal recessive trait. Clin Genet. 1976 Jan;9(1):8–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1976.tb01543.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viljoen D. L., Smart R. Split-foot anomaly, microphthalmia, cleft-lip and cleft-palate, and mental retardation associated with a chromosome 6;13 translocation. Clin Dysmorphol. 1993 Jul;2(3):274–277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiffenbach B., Falls K., Bricker A., Hall L., McMahon J., Wasmuth J., Funanage V., Donis-Keller H. A genetic linkage map of human chromosome 5 with 60 RFLP loci. Genomics. 1991 May;10(1):173–185. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90498-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissenbach J., Gyapay G., Dib C., Vignal A., Morissette J., Millasseau P., Vaysseix G., Lathrop M. A second-generation linkage map of the human genome. Nature. 1992 Oct 29;359(6398):794–801. doi: 10.1038/359794a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]