Abstract
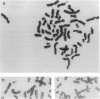
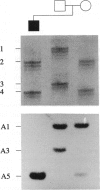
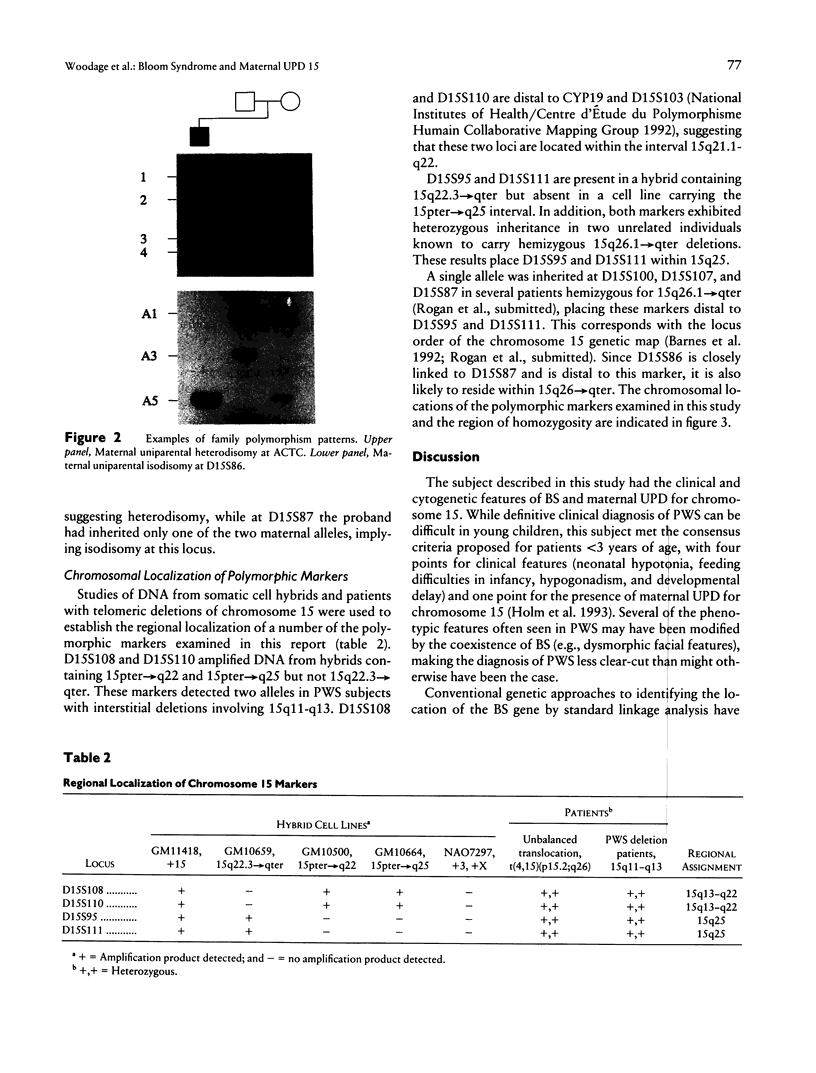
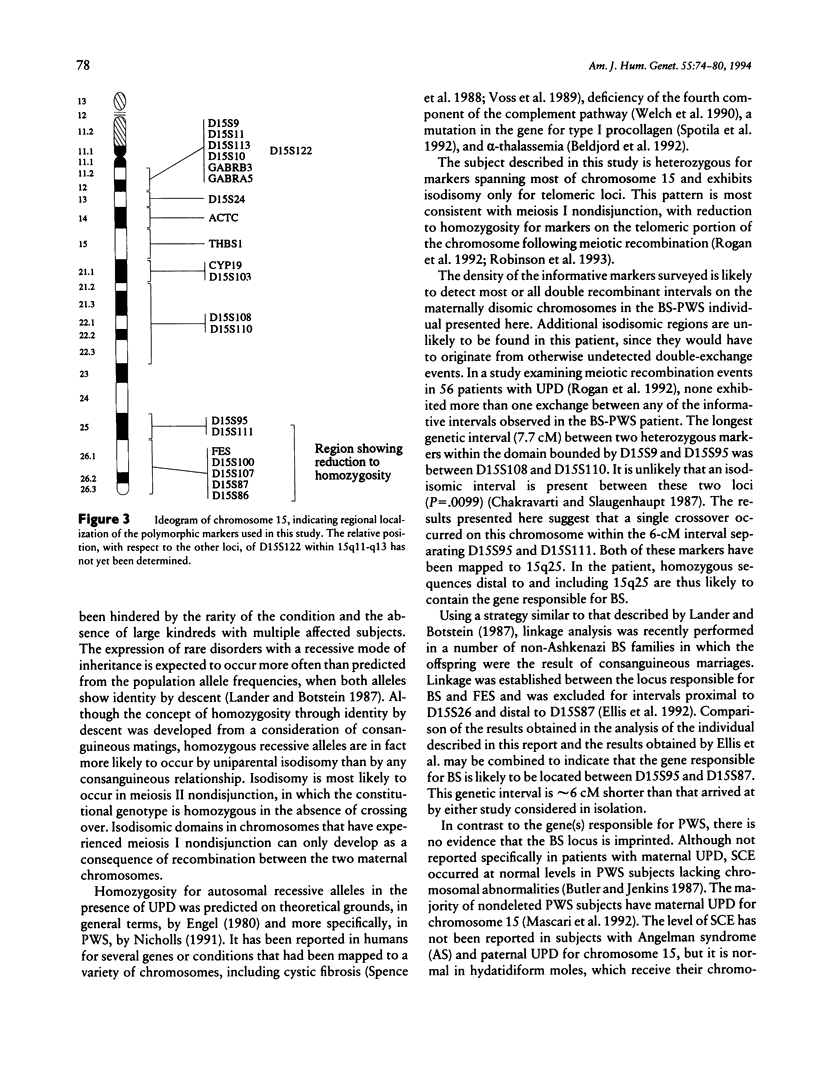
Bloom syndrome (BS) is an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by increases in the frequency of sister-chromatid exchange and in the incidence of malignancy. Chromosome-transfer studies have shown the BS locus to map to chromosome 15q. This report describes a subject with features of both BS and Prader-Willi syndrome (PWS). Molecular analysis showed maternal uniparental disomy for chromosome 15. Meiotic recombination between the two disomic chromosomes 15 has resulted in heterodisomy for proximal 15q and isodisomy for distal 15q. In this individual BS is probably due to homozygosity for a gene that is telomeric to D15S95 (15q25), rather than to genetic imprinting, the mechanism responsible for the development of PWS. This report represents the first application of disomy analysis to the regional localization of a disease gene. This strategy promises to be useful in the genetic mapping of other uncommon autosomal recessive conditions.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aaltonen L. A., Peltomäki P., Leach F. S., Sistonen P., Pylkkänen L., Mecklin J. P., Järvinen H., Powell S. M., Jen J., Hamilton S. R. Clues to the pathogenesis of familial colorectal cancer. Science. 1993 May 7;260(5109):812–816. doi: 10.1126/science.8484121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker R. A., Surti U., Wenger S. L. Sister chromatid exchange and chromosome breakage in complete hydatidiform moles. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1992 Aug;62(1):53–57. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(92)90039-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beldjord C., Henry I., Bennani C., Vanhaeke D., Labie D. Uniparental disomy: a novel mechanism for thalassemia major. Blood. 1992 Jul 1;80(1):287–289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budowle B., Chakraborty R., Giusti A. M., Eisenberg A. J., Allen R. C. Analysis of the VNTR locus D1S80 by the PCR followed by high-resolution PAGE. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Jan;48(1):137–144. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler M. G., Jenkins B. B. Sister chromatid exchange analysis in the Prader-Labhart-Willi syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1987 Dec;28(4):821–827. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320280406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakravarti A., Slaugenhaupt S. A. Methods for studying recombination on chromosomes that undergo nondisjunction. Genomics. 1987 Sep;1(1):35–42. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(87)90102-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel E. A new genetic concept: uniparental disomy and its potential effect, isodisomy. Am J Med Genet. 1980;6(2):137–143. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320060207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishel R., Lescoe M. K., Rao M. R., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A., Garber J., Kane M., Kolodner R. The human mutator gene homolog MSH2 and its association with hereditary nonpolyposis colon cancer. Cell. 1993 Dec 3;75(5):1027–1038. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90546-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- German J., Passarge E. Bloom's syndrome. XII. Report from the Registry for 1987. Clin Genet. 1989 Jan;35(1):57–69. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1989.tb02905.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groden J., German J. Bloom's syndrome. XVIII. Hypermutability at a tandem-repeat locus. Hum Genet. 1992 Dec;90(4):360–367. doi: 10.1007/BF00220459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holm V. A., Cassidy S. B., Butler M. G., Hanchett J. M., Greenswag L. R., Whitman B. Y., Greenberg F. Prader-Willi syndrome: consensus diagnostic criteria. Pediatrics. 1993 Feb;91(2):398–402. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn E. M., Therman E. Cytogenetics of Bloom's syndrome. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1986 May;22(1):1–18. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(86)90132-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander E. S., Botstein D. Homozygosity mapping: a way to map human recessive traits with the DNA of inbred children. Science. 1987 Jun 19;236(4808):1567–1570. doi: 10.1126/science.2884728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leach F. S., Nicolaides N. C., Papadopoulos N., Liu B., Jen J., Parsons R., Peltomäki P., Sistonen P., Aaltonen L. A., Nyström-Lahti M. Mutations of a mutS homolog in hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer. Cell. 1993 Dec 17;75(6):1215–1225. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90330-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindblom A., Tannergård P., Werelius B., Nordenskjöld M. Genetic mapping of a second locus predisposing to hereditary non-polyposis colon cancer. Nat Genet. 1993 Nov;5(3):279–282. doi: 10.1038/ng1193-279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mascari M. J., Gottlieb W., Rogan P. K., Butler M. G., Waller D. A., Armour J. A., Jeffreys A. J., Ladda R. L., Nicholls R. D. The frequency of uniparental disomy in Prader-Willi syndrome. Implications for molecular diagnosis. N Engl J Med. 1992 Jun 11;326(24):1599–1607. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199206113262404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDaniel L. D., Schultz R. A. Elevated sister chromatid exchange phenotype of Bloom syndrome cells is complemented by human chromosome 15. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 1;89(17):7968–7972. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.17.7968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls R. D., Knoll J. H., Butler M. G., Karam S., Lalande M. Genetic imprinting suggested by maternal heterodisomy in nondeletion Prader-Willi syndrome. Nature. 1989 Nov 16;342(6247):281–285. doi: 10.1038/342281a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls R. D. Uniparental disomy as the basis for an association of rare disorders. Am J Med Genet. 1991 Nov 1;41(2):273–274. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320410233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peltomäki P., Aaltonen L. A., Sistonen P., Pylkkänen L., Mecklin J. P., Järvinen H., Green J. S., Jass J. R., Weber J. L., Leach F. S. Genetic mapping of a locus predisposing to human colorectal cancer. Science. 1993 May 7;260(5109):810–812. doi: 10.1126/science.8484120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry P., Wolff S. New Giemsa method for the differential staining of sister chromatids. Nature. 1974 Sep 13;251(5471):156–158. doi: 10.1038/251156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinchik E. M., Bultman S. J., Horsthemke B., Lee S. T., Strunk K. M., Spritz R. A., Avidano K. M., Jong M. T., Nicholls R. D. A gene for the mouse pink-eyed dilution locus and for human type II oculocutaneous albinism. Nature. 1993 Jan 7;361(6407):72–76. doi: 10.1038/361072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson W. P., Bernasconi F., Mutirangura A., Ledbetter D. H., Langlois S., Malcolm S., Morris M. A., Schinzel A. A. Nondisjunction of chromosome 15: origin and recombination. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Sep;53(3):740–751. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spence J. E., Perciaccante R. G., Greig G. M., Willard H. F., Ledbetter D. H., Hejtmancik J. F., Pollack M. S., O'Brien W. E., Beaudet A. L. Uniparental disomy as a mechanism for human genetic disease. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Feb;42(2):217–226. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spotila L. D., Sereda L., Prockop D. J. Partial isodisomy for maternal chromosome 7 and short stature in an individual with a mutation at the COL1A2 locus. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Dec;51(6):1396–1405. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trent R. J., Volpato F., Smith A., Lindeman R., Wong M. K., Warne G., Haan E. Molecular and cytogenetic studies of the Prader-Willi syndrome. J Med Genet. 1991 Oct;28(10):649–654. doi: 10.1136/jmg.28.10.649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voss R., Ben-Simon E., Avital A., Godfrey S., Zlotogora J., Dagan J., Tikochinski Y., Hillel J. Isodisomy of chromosome 7 in a patient with cystic fibrosis: could uniparental disomy be common in humans? Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Sep;45(3):373–380. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J. L., May P. E. Abundant class of human DNA polymorphisms which can be typed using the polymerase chain reaction. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Mar;44(3):388–396. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weksberg R., Smith C., Anson-Cartwright L., Maloney K. Bloom syndrome: a single complementation group defines patients of diverse ethnic origin. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Jun;42(6):816–824. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch T. R., Beischel L. S., Choi E., Balakrishnan K., Bishof N. A. Uniparental isodisomy 6 associated with deficiency of the fourth component of complement. J Clin Invest. 1990 Aug;86(2):675–678. doi: 10.1172/JCI114760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yunis J. J. High resolution of human chromosomes. Science. 1976 Mar 26;191(4233):1268–1270. doi: 10.1126/science.1257746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]