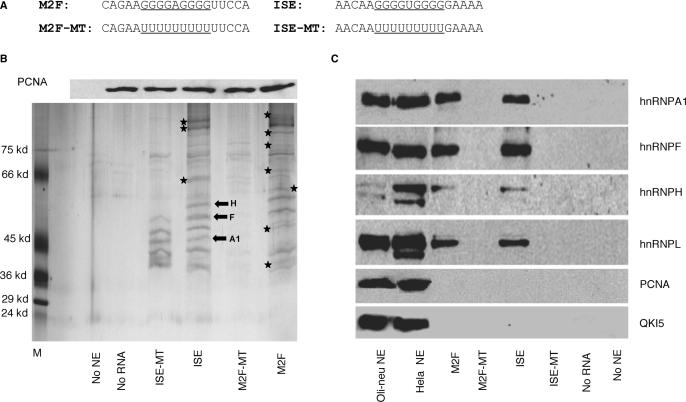
Figure 6.
Biochemical analysis of proteins that bind to M2F and ISE in Oli-neu extracts. (A) RNA templates used in RNA affinity precipitations. The natural G-rich sequences and the mutated poly-U sequences are underlined. (B) Upper panel: Western blot analysis of PCNA levels in each RNA affinity precipitate. One-tenth of each RNA/protein mixture prior to streptavidin beads precipitation was separated by SDS-PAGE and probed with an antibody to PCNA. Lower panel: representative silver stained gel of RNA affinity precipitates with biotinylated RNA templates containing wild-type (M2F and ISE), poly-U (M2F-MT and ISE-MT) and Oli-neu extracts (n = 2) (see Materials and Methods section). Controls are precipitates without nuclear extracts (no NE) and without RNA template (no RNA). The asterisks indicate protein bands that are uniquely present in precipitates with either M2F or ISE. The block arrows indicate the protein bands that were analyzed by LC/MS/MS and their identity is shown. (C). Western blot analysis of hnRNPA1, F, H and L in the RNA affinity precipitates (see Materials and Methods Section). Precipitates without nuclear extracts (no NE) and without RNA template (no RNA) are used as controls. Western blot of Oli-neu and HeLa nuclear extracts (9 μg) were used as control for the reactivity of the antibody. PCNA and QKI5 antibodies, used as control of the specificity of RNA affinity precipitates, detect a band in the nuclear extracts, but not in the RNA affinity precipitates.