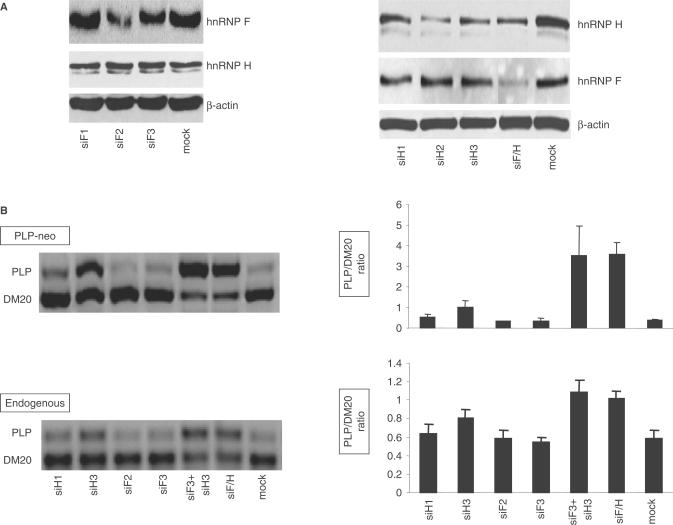
Figure 8.
RNAi-mediated knock down of hnRNPH and F increases the PLP/DM20 ratio in Oli-neu cells. (A) Representative Western blot of cell extracts prepared from Oli-neu cells treated with siRNAs that target hnRNPH (siH1, H2, H3), hnRNPF (siF1, F2 and F3) and both H and F (siF/H). Mock are cells treated with negative control siRNA. After quantification of the bands, the values were corrected by actin, used as control for loading accuracy. The hnRNPH was reduced by 40, 70 and 50% in cells treated with siH1, siH2 and siH3 and 50% in cells treated with siH/F versus control (n = 2). The hnRNPF was reduced by 60 and 40% in cells treated with siF2 and siF3 and by 60% in cells treated with siF/H versus controls. (B) Representative RT-PCR analysis of the PLP-neo derived PLP and DM20 spliced products and the endogenous PLP and DM20 transcripts amplified from RNA isolated from Oli-neu cells treated with siH1, siH3, siF2, siF3, siF3 + H3 and siF/H (35 PCR cycles). The bar graph shows the PLP/DM20 ratios ± SD (n = 3). Mock are cells treated with control siRNA. Increase in PLP/DM20 ratio is statistically significant for siH3 (P < 0.05) and for siF3+H3 and siF/H (P < 0.01)-treated cells compared with mock-treated cells.