Figure 9.
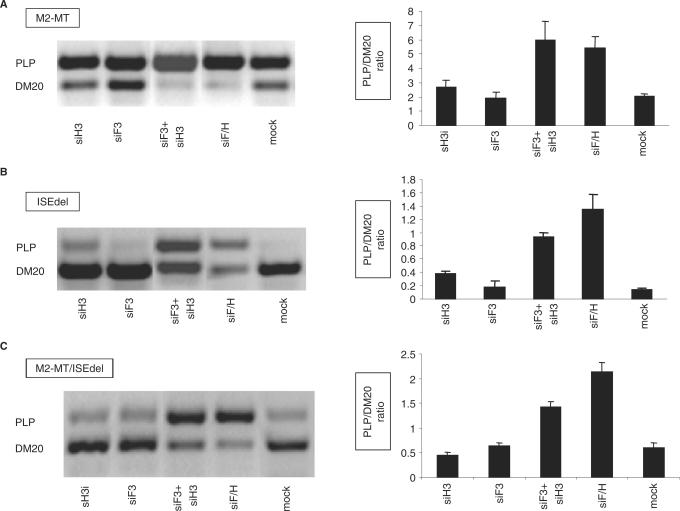
The effect of mutation of M2 and ISE on the hnRNPH and F-mediated regulation of PLP/DM20. (A) Representative RT-PCR analysis of the M2-MT derived PLP and DM20 products amplified from RNA isolated from Oli-neu cells treated with siH3, siF3, siF3+H3, siF/H (35 PCR cycles). Mock are cells treated with control siRNA. The bar graph shows the PLP/DM20 ratios ± SD (n = 3). The increase in PLP/DM20 ratio induced by siF3+H3 and siF/H are statistically significant (P < 0.01). (B) Representative RT-PCR analysis of the ISEdel derived PLP and DM20 products amplified from RNA prepared from Oli-neu cells treated with siH3, siF3, siF3+H3, siF/H (35 PCR cycles). Mock are cells treated with control siRNA. The bar graph shows the PLP/DM20 ratios ± SD (n = 3). The increase in PLP/DM20 ratio induced by siH3, siF3+H3 and siF/H is statistically significant (P < 0.01). (C) Representative RT-PCR analysis of the M2-MT/ISEdel derived PLP and DM20 products amplified from RNA prepared from Oli-neu cells treated with siH3, siF3, siF3+H3, siF/H (35 PCR cycles). Mock are cells treated with control siRNA. The bar graph shows the PLP/DM20 ratios ± SD (n = 3). The changes in PLP/DM20 ratio induced by siF3+H3 and siF/H are statistically significant (P < 0.05).