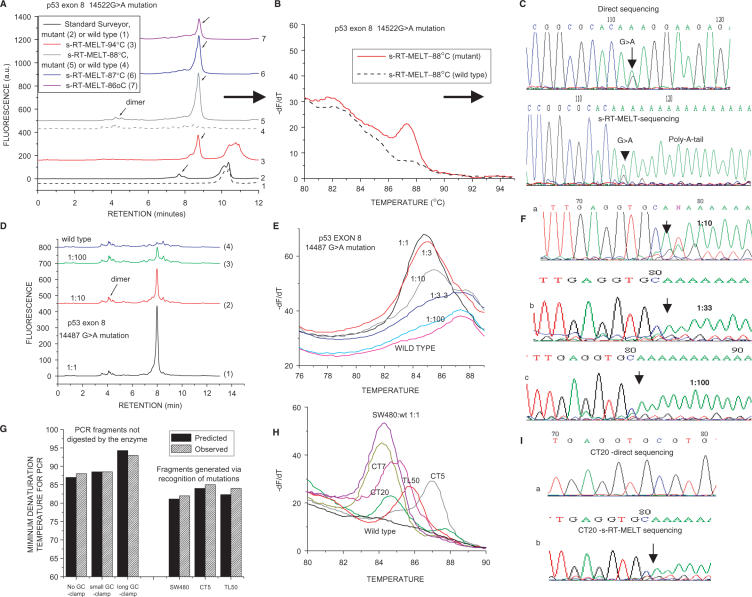
Figure 2.
Detection of p53 exon 8 mutations using s-RT-MELT. (A) dHPLC chromatograms of the products obtained using the standard Surveyor™-dHPLC approach (28), versus the new technology on a sample containing a p53 exon 8 14522G > A mutation or a wild-type sample. Curves 1 and 2: Standard Surveyor™-dHPLC on wild- type and mutant samples, respectively. Curves 3–7: s-RT-MELT products when real-time PCR is performed at different denaturation temperatures. (B) Real-time differential melting curves for a PCR denaturation temperature of 88°C. (C) Sequencing of the s-RT-MELT-generated PCR fragment for a PCR denaturation temperature of 88°C. Direct sequencing of the same PCR product from genomic DNA is also depicted. D. dHPLC chromatograms of s-RT-MELT products obtained using serial dilution of DNA from SW480 cells in wild-type DNA. Real-time PCR was performed at 88°C denaturation temperature. (E) Melting curve analysis of the s-RT-MELT products obtained using serial dilution of SW480 in wild-type DNA at 88°C denaturation temperature. (F) s-RT-MELT-sequencing of s-RT-MELT products obtained using serial dilution of SW480 in wild-type DNA. (G) Predicted-versus-observed minimum denaturation temperatures for generation of s-RT-MELT products following real-time PCR. The influence of the GC-clamp length (no GC-clamp; 26-nt GC-clamp; or 117-nt GC-clamp), and the position of the mutation along the sequence are depicted. (H) s-RT-MELT screening of unknown p53 exon 8 mutations of 48 colon and lung tumor DNA: representative results from mutation-positive samples and wild-type sample are depicted. (I) Sequencing of low-level p53 exon 8 mutation (colon tumor sample CT20) by direct sequencing and by s-RT-MELT sequencing.