Figure 2.
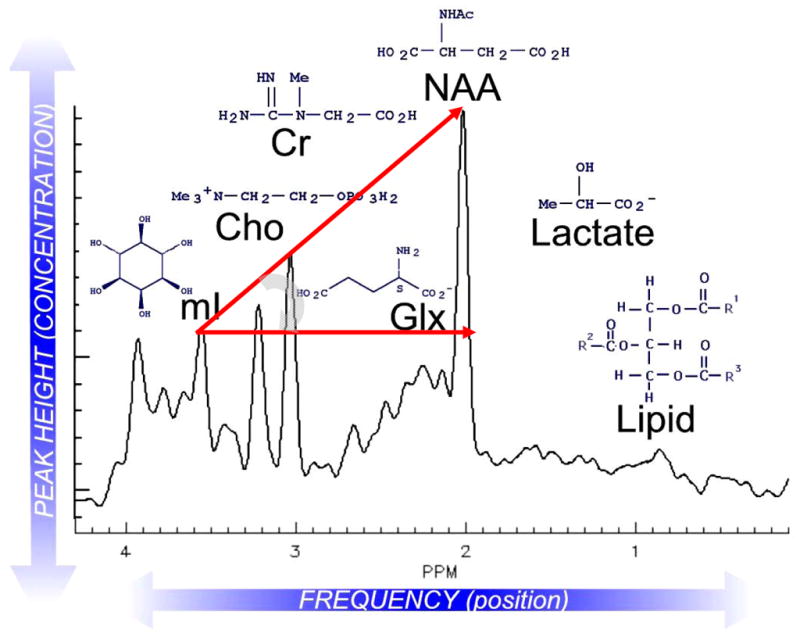
Representative proton MRS spectrum of normal human brain with major peaks of interest depicted. Lactate and lipid signals are absent from this spectrum of a healthy individual. Hunter’s angle (HA; curved gray arrow) refers to the approximate 45-degree angle formed by the peaks myo-inositol (mI), creatine (Cr), choline (Cho), and NAA, when they are present in normal proportions (NAA/Cr ~1.5, Cho/Cr ~0.75; mI/Cr ~0.5) using short-echo-stimulated echo acquisition mode (STEAM) spectroscopy. Changes in HA can be applied to such common MRS diagnoses as tumor (HA < − 50°), stroke, Alzheimer disease (HA ~ 15°), neonatal hypoxia (HA ~ − 45°) or AIDS-related progressive multifocal leukomalacia (HA ~ 0°). Glx = glutamine and glutamate. Reprinted with permission, NeuroRx (Lin et al., 2005).
