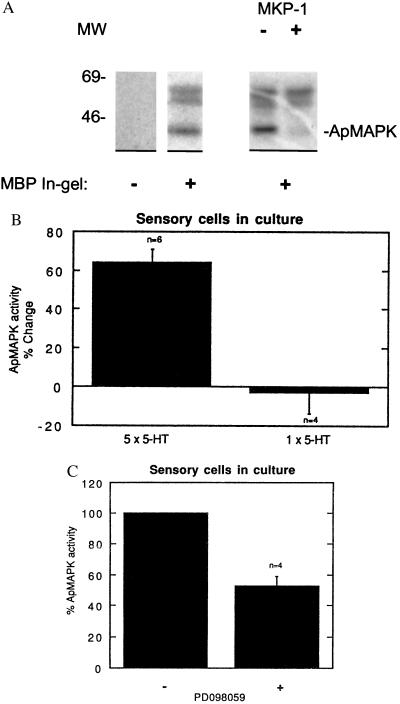
Figure 2.
Repeated application of 5-HT onto sensory cells in culture activates apMAPK. Protein extracts from approximately 50 cells in culture were subjected to a kinase assay in MBP-containing gels (A–C, except where otherwise indicated). (A) An extract of Aplysia sensory cells in buffer A and 0.3 mg/ml BSA was treated with 1 μl of the pure MAPK phosphatase 1 (MKP-1) prior to the kinase assay in MBP-containing gels. (B) Five pulses of 10 μM 5-HT were given to sensory cells for 5 min, each pulse at 20-min intervals, while control cultures were given regular medium at the same intervals. An in-gel kinase assay was subsequently performed. The kinase activities at 58 and 63 kDa were used as references to correct and normalize for the apMAPK activities. Normalized MAPK activity as detected by the in-gel kinase assay was 64% higher in cultures treated with five pulses of 5-HT compared with control (mock treated) cultures. Also, similar experiments were performed with one pulse of 5-HT that lasted 5 min. The mean apMAPK activity after one pulse compared with control cultures was 2.7 ± 10.8%; P < 0.01 vs. five pulses of 5-HT. (C) Sensory cells in culture were treated with 30 μM PD098059 for 30 min or with vehicle (0.1% dimethyl sulfoxide) and apMAPK activity was determined by kinase analysis in MBP-containing gels. Shown is mean percentage ±SE.