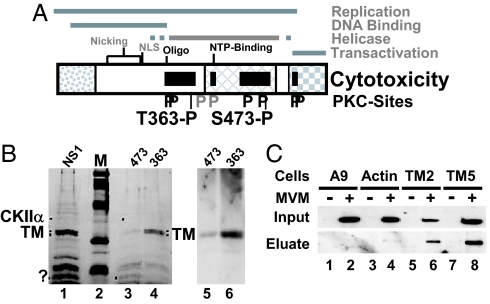
Fig. 1.
Determinants of NS1-induced cytotoxicity. (A) Domain structure of NS1 (5). The common N terminus of NS1 and NS2, the region of homology with the SV40 large T-antigen, and the trans activation domain are represented, respectively, as dotted, cross-hatched, and checkered boxes. The nucleotide-binding (NTP-binding) site, the oligomerization region (Oligo), the nuclear localization signal (NLS), and nicking motifs (metal coordination site and linkage tyrosine) are positioned. Black bars denote NS1 regions mediating cytopathogenicity. Consensus PKC-phosphorylation sites that modulate (black P) or do not modulate (gray P) CPE are indicated, including 363-P and 473-P targeted for differential affinity chromatography. (.B Left) SDS/PAGE and Coomassie blue staining of proteins eluted from GST-NS1 affinity columns. NS1, proteins in A9-P3-DE1 binding to GST-NS1WT; 473, proteins lacking affinity for GST-NS1:S473A and binding to GST-NS1WT; 363, proteins lacking affinity for GST-NS1:T363A and binding to GST-NS1WT. M, molecular mass markers (97, 66, 45, 30, and 20.1 kDa (Rainbow marker, Amersham). Proteins overrepresented in either 474 or 363 are marked with dots. The doublet marked TM was cut from the gel and subjected to MS/MS analysis. (Right) Western blot analyses of both flow-through samples with TM-specific antibodies. (C) Interaction of NS1 with TM in MVM-infected cells. Binding of NS1 to cytoskeletal proteins was estimated on the basis of its affinity for GST-tagged TM2, TM5, and β-actin. Cell extracts from (MVM-infected) A9 cells (lanes 1 and 2) or from derivatives expressing GST-tagged cytoskeleton proteins (β-actin, lanes 3 and 4; TM2, lanes 5 and 6; TM5, lanes 7 and 8) were run through glutathione–Sepharose columns specifically retaining GST-tagged proteins. Binding partners (e.g., NS1) of GST-tagged proteins were eluted with 700 mM NaCl (eluate) and analyzed by Western blotting with anti-NS1C compared with total amounts (input).