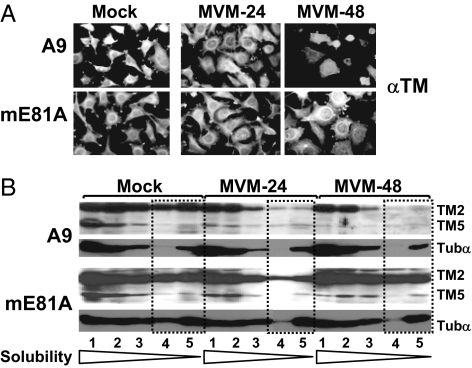
Fig. 3.
Effect of CKIIα functional modifications on MVM-induced cytoskeleton alterations. A9 or A9:P38-CKII(mE81A) cells were infected (or not) with MVM (30 pfu per cell). (A) For immunofluorescence microscopy, cells were fixed with paraformaldehyde at the indicated time after infection, and the TM filament network was revealed by indirect fluorescence microscopy. (B) For biochemical characterization of cytoskeletal filaments, extracts were fractionated according to their differential solubility in detergent(s) as described in Materials and Methods,“ and the individual fractions (S1–S5) were analyzed for TM and tubulin α by Western blotting. Low-solubility fractions corresponding to rigid fiber structures are framed by dotted lines. The migration of TM2, TM5, and tubulin α (Tubα) are indicated.