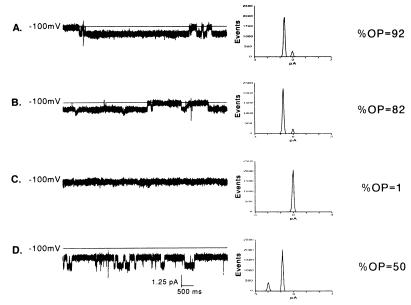
Figure 4.
Blockade of channel activity with the polyanion heparan sulfate. Continuous 10-s traces (Left), histograms of the distribution of current (Middle), and open probability (Right) in which two doses of heparan sulfate were used to block channel activity. Traces were obtained at a holding potential of −100 mV in an experimental buffer containing 200 mM CsCl and 5 μM S-Oligo (pH 7.4). Heparan sulfate produced a dose-dependent decrease in open probability. Addition of heparan sulfate at 10 μg/ml to both solution chambers decreased open probability from 0.92 (A) to 0.82 (B). Channel activity was completely blocked when heparan sulfate was increased in both chambers to 20 μg/ml (C). Channel activity was restored when heparan sulfate was washed from both chambers (D).