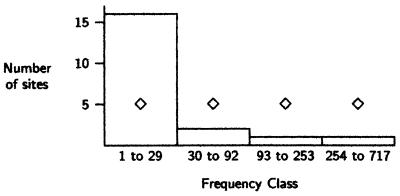
Figure 8.
Frequency spectrum and mismatch distribution from a world sample of 718 Y chromosome sequences. There are 20 segregating sites ascertained at approximately 20,000 positions. Ascertainment was done in two samples, one with 21 chromosomes and one with 53. If a site has population frequency x, then the probability that it will be detected in a sample of size n, the ascertainment function, is 1 − (xn + (1 − x)n). Diamonds show the expected number of sites in each frequency class under the hypothesis of constant population size, computed by multiplying the ascertainment function by the distribution in Eq. 1. The excess of low frequency sites is consistent with a Pleistocene population expansion. Because the whole nonrecombining portion of the Y chromosome is a single locus, these sites are not independent, and there is no simple statistical test of the constant size hypothesis.