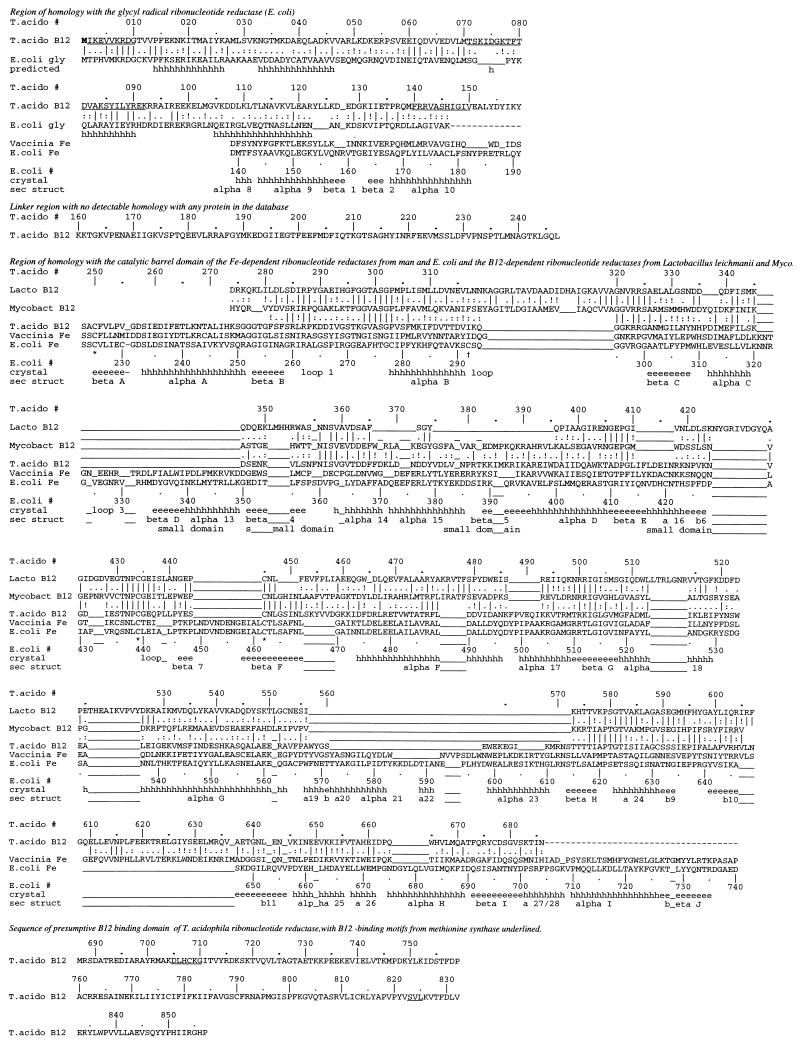
Figure 1.
Sequence of the B12-dependent ribonucleotide reductase (RNR, EC 1.17.4.2) from T. acidophila aligned with other proteins. T.acido #, sequential numbering of sequence of B12-dependent ribonucleotide reductase from T. acidophila; T.acido B12, sequence of the B12-dependent RNR from T. acidophila (GenBank accession no. U73619U73619); E. coli gly, sequence of the glycyl radical-dependent anaerobic RNR from E. coli (GenBank accession no. P289093); Vaccinia Fe, sequence of the catalytic subunit of the Fe-dependent RNR from vaccinia virus (strain Copenhagen; GenBank accession no. P20503P20503; Lacto B12, sequence of the B12-dependent RNR from Lactobacillus leichmannii (7); Mycobact B12, sequence of the presumed B12-dependent RNR (Gene 50 protein) from mycobacteriophage L5 (GenBank accession no. Q05262Q05262); E. coli #, sequential numbering of the sequence of the Fe-dependent ribonucleotide reductase from E. coli, corresponding to numbering in ref. 24; pred, secondary structure (h = helix; e = strand) predicted by method in refs. 17, 25, and 26; crystal secondary structure, secondary structure (h = α-helix; e = β-strand) determined by crystallography (24) for the E. coli enzyme, with designation of the secondary structure below. Multiple alignment was from DARWIN (12, 27). Gaps are not moved to reflect experimental or predicted structures. A dash indicates insignificant sequence similarity, and an underscore indicates deletion. Underlined sequences in T. acidophila RNR are peptide sequences of CNBr peptide fragments. Cysteines involved in catalysis (Cys-225, Cys-462, and Cys-439) are marked with an asterisk. The cysteine in the regulatory site is marked by a dagger (28).