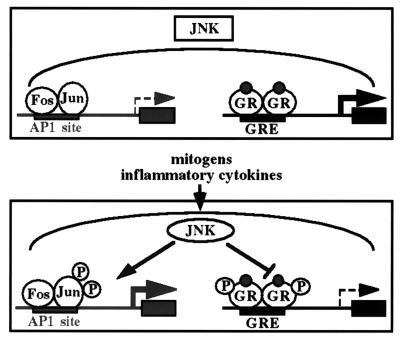
Figure 7.
Model for reciprocal regulation of GR and AP-1 transcriptional activation by JNK. Under conditions where JNK is inactive, AP-1-mediated transcription is low because c-Jun is not phosphorylated at sites required for full transcriptional activity, whereas hormone-induced GR-dependent transcription is high, as GR is not phosphorylated at the inhibitory site Ser-246. In the presence of growth factors or inflammatory cytokines, JNK is activated and phosphorylates both c-Jun and GR, which results in an increase in AP-1-mediated transcriptional activation and a decrease in GR-dependent transcriptional enhancement. The ability of activated JNK to affect the transcriptional activity of AP-1 and GR oppositely provides a mechanism to ensure the rapid inhibition of GR-dependent gene expression when it conflicts with mitogenic or proinflammatory signals.