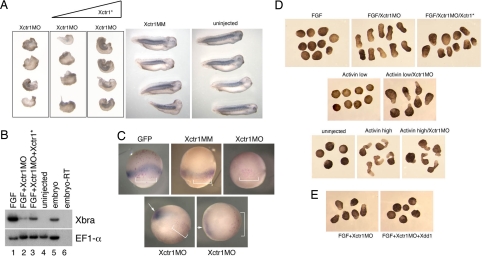
Fig. 2.
Xctr1 knockdown inhibits differentiation and enhances morphogenesis. (A) Whole-mount immunohistochemistry of stage 32 embryos injected in the dorsal marginal zone at early cleavage stages with 250 ng of either Xctr1MO or Xctr1 5 base-pair mismatch (MM) morpholinos. Rescue experiments were performed by coexpression of a morpholino-insensitive Xctr1 construct (Xctr1*) in which the Xctr1MO-binding region was separated from the remainder of Xctr1 by 6 Myc epitope tags; somite formation was scored on a scale of 0 to 5 (0, complete, bilateral absence of 12/101 stain; 5, normal staining and somite morphology). Xctr1MO embryos were scored as 1.49 ± 0.3 (n = 41), and Xctr1MO + 500-pg Xctr1* embryos were scored as 2.01 ± 0.07 (n = 39). Xctr1* RNA (250 and 500 pg) were coinjected with Xctr1MO as indicated. (B) Effect of Xctr1 knockdown on FGF-mediated induction of Xbrachyury (Xbra) expression and its rescue by coexpression of 500 pg of Xctr1* RNA. Xctr1*, like Xctr1, induces expression of the neural marker NRP-1, albeit at higher doses than wild-type (data not shown). (C) Xctr1 knockdown inhibits Xbra expression in vivo. Whole-mount in situ hybridization analysis of gastrula-stage embryos using an antisense Xbra probe. Red-gal staining used as a lineage trace is demarcated with brackets; Xbra stain in Xctr1MO-injected embryos is indicated with arrows. (Upper) Marginal views. (Lower) Vegetal views. (D) Effects of Xctr1 knockdown on FGF- and activin-mediated morphogenesis of stage 20 animal caps. (E) Expression of dominant-negative Dishevelled (Xdd1) RNA inhibits Xctr1 knockdown-mediated elongation by FGF; 10 ng/ml FGF and 0.5 ng/ml (high) or 0.1 ng/ml (low) activin was added as indicated.