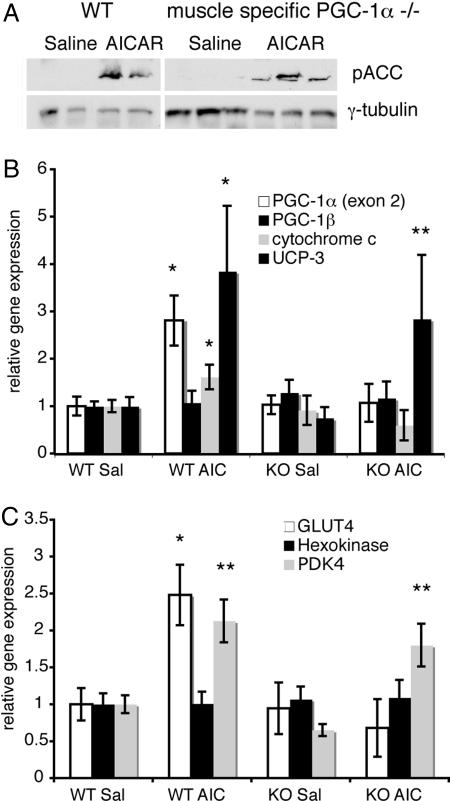
Fig. 3.
AMPK-driven increase in PGC-1α, GLUT4, and cytochrome c gene expression requires PGC-1α protein in vivo. (A) AMPK is activated in skeletal muscle of AICAR-injected mice. Levels of ACC protein phosphorylated at serine-79 in gastrocnemeus muscle from WT and PGC-1α muscle-specific knockout (KO) mice, injected with saline or AICAR are shown. (B) Injection of AICAR induces the mRNA expression of PGC-1α and cytochrome c but not PGC-1β in the skeletal muscle of WT mice (∗, P < 0.01); this induction does not occur in the skeletal muscle of the muscle-specific PGC-1α −/− mice. UCP-3 gene expression is also increased in the muscle-specific PGC-1α −/− mice (∗∗, P < 0.05). (C) Injection of AICAR induces the mRNA expression of GLUT4 (∗, P < 0.01) and PDK4 (∗∗, P < 0.1) but not of hexokinase in the skeletal muscle of WT mice. PDK4 gene expression increases also in the muscle-specific PGC-1α −/− mice. Female mice were injected with either saline or 250 mg/kg AICAR. Skeletal muscle was harvested after 6 h, and gene expression was measured by using semiquantitative PCR (n = 5–7).