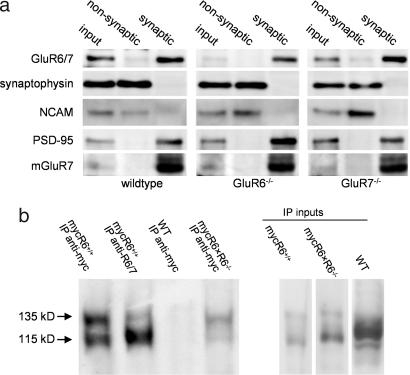
Fig. 3.
Subcellular localization and association of GluR6 and GluR7 subunits. (a) Immunoblots of hippocampal synaptosomal membranes (input) and from nonsynaptic and synaptic fractions prepared from WT, GluR6−/−, and GluR7−/− mice. PSD95, a characteristic protein of the postsynaptic density, was present in the synaptic junctions but excluded from the nonsynaptic fraction. The same separation occurred with the metabotropic receptor mGluR7, which is known to be present almost exclusively within the presynaptic active zone (21). On the contrary, the adhesion molecule NCAM and the synaptic vesicle protein synaptophysin were detected only in the nonsynaptic fraction. Analysis of the protein fractions with an anti-GluR6/7 antibody revealed that, in the absence of the GluR6 subunit, GluR7 is found at synapses, and vice versa. (b) KARs were purified by immunoprecipitation from mouse brains of different genotypes (WT, mycGluR6, and mycGluR6×GluR6−/−), with an anti-myc antibody. Western blots were probed with an anti-GluR6/7 antibody. In brains from mycGluR6×GluR6−/− mice, the upper band (135 kDa) corresponds to the immunoprecipitated transgene product (myc-GluR6a) and the lower band (115 kDa) to GluR7.