Figure 3. Octamer dissociation from DNA could be caused by closely spaced PolII molecules.
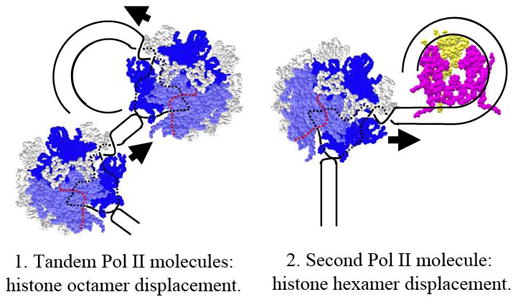
Dissociation of the octamer could occur by the following mechanisms: (1) When PolII molecules are closely spaced, the second molecule could prevent DNA-octamer re-association behind the first transcribing PolII molecule and thus prevent formation of the intermediate 2 (Fig. 2). This would substantially decrease the number of DNA-histone interactions and could cause octamer dissociation from DNA. (2) Alternatively, second molecule of PolII could approach the hexasome that was just transcribed and therefore the complete nucleosome was not recovered yet. Since the hexasome is stabilized by considerably smaller number of DNA-histone interactions, the histone hexamer could be displaced from DNA by the second molecule of PolII. The second model does not require very close spacing of PolII molecules.
