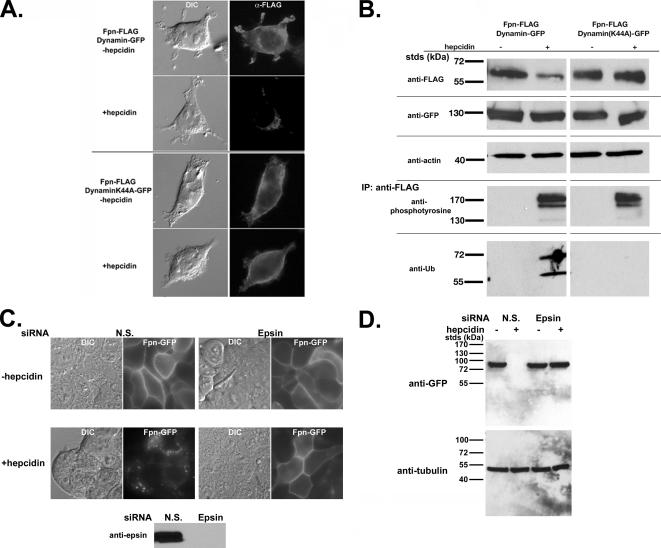
Figure 2.
Fpn is phosphorylated at the plasma membrane. (A) HEK293T cells were transiently transfected with Fpn-FLAG and either Dynamin-GFP or DynaminK44A-GFP. Cells were incubated in the presence or absence of 1 μg/ml hepcidin for 60 min and processed for immunofluorescence using mouse anti-FLAG followed by Alexa 594-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG (1:750) as secondary antibody. (B) HEK293T cells were transiently transfected as described in A. Cells were incubated in the presence or absence of 1 μg/ml hepcidin as in A, extracts obtained as described in Figure 1 and Western blotted for Fpn-FLAG, Dynamin-GFP, and actin (loading control). Extracts were immunoprecipitated using anti-FLAG resin (M2), and the immunoprecipitates were examined for the presence of tyrosine phosphorylated Fpn-FLAG or ubiquitinated Fpn-FLAG by using mouse anti-phosphotyrosine or mouse anti-ubiquitin antibodies followed by peroxidase-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG. (C and D) HEK293T Fpn-GFP cells were transfected with nonspecific (NS) or epsin-specific siRNA oligonucleotide pools. After 48 h of incubation, cells were induced to express Fpn-GFP and then 18 h later 1 μg/ml hepcidin was added for 1 h. The efficiency of epsin depletion was assessed by Western blot analysis using antibodies to epsin. The presence of Fpn-GFP was assessed by epifluorescence (C) and Western blot analysis (D).