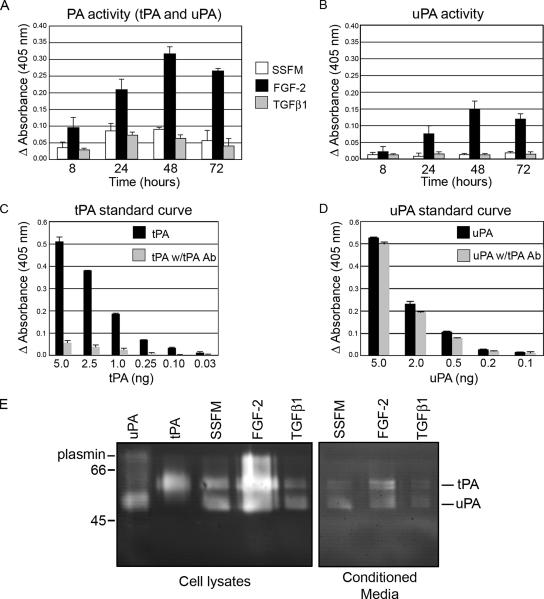
Figure 2.
PA activity and expression are increased with FGF-2 and decreased with TGFβ treatment. Cellular PA activity was increased with FGF-2 treatment and inhibited by TGFβ1. (A) Cells were plated in SSFM, SSFM-FGF, or SSFM-TGFβ, and they were grown for 8, 24, 48, or 72 h. At the specified time points, cells were washed two times with PBS, and then they were lysed with 0.5 ml of 0.1 M Tris-HCl, pH 8.1 with 0.1% Triton X-100. PA activity was determined with a chromogenic assay that detected the generation of plasmin. (B) The same samples were incubated with an inhibitory tPA antibody to determine the proportion of PA activity that was uPA and tPA. (C) tPA standard curve without and with inhibitory tPA antibody. (D) uPA standard curve without and with inhibitory tPA antibody. (E) Fibroblasts were plated in SSFM, SSFM-FGF, or SSFM-TGFβ. After 72 h, lysates and conditioned media were tested for PA activity. uPA and tPA in lysates and conditioned media were increased in FGF-2–treated cells, whereas less uPA and tPA was detected in TGFβ1 treated cells. The PA assay was performed in duplicate with cells from three different donors. The zymogram is representative of three experiments with the same cells as in the PA assay (A and B).