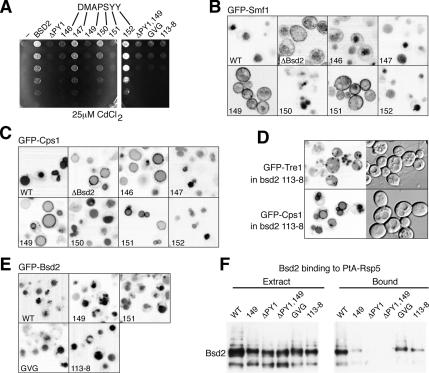
Figure 3.
Mutation of sequences within the cytoplasmic domain of Bsd2. (A) Growth of a Δbsd2 strain in the presence of 25 μM CdCl2, complemented with either control vector (−), wild-type BSD2 (BSD2), Y140A (ΔPY1), D146A (146), M147A (147), P149A (149), S150A (150), Y151A (151), Y152A (152), Y140A/P149A (ΔPY1,149), G170A/V173A/G174A (GVG), or D113A/G114A/V115A/F116A/S117A/N118A (113-8) BSD2 mutants. (B) Localization of GFP-Smf1ΔN and (C) GFP-Cps1 in a Δbsd2 yeast strain complemented with wild-type (WT), control plasmid (ΔBsd2), or plasmids expressing D146A (146), M147A (147), P149A (149), S150A (150), Y151A (151), or Y152A (152) forms of Bsd2. (D) Localization of GFP-Tre1 and GFP-Cps1 in a Δbsd2 strain expressing 113-8 Bsd2. (E) Localization in a Δbsd2Δtul1 strain of GFP tagged wild-type Bsd2 (WT), P149A (149), Y151A (151) G170A/V173A/G174A (GVG), or D113A/G114A/V115A/F116A/S117A/N118A (113-8) Bsd2 mutants. (F) Immunoprecipitation of Triple HA-tagged Bsd2 mutant proteins with protein-A tagged Rsp5 from Δbsd2Δpep4 cells. IgG-Sepharose eluates were enriched over the extracts by a factor of 20.