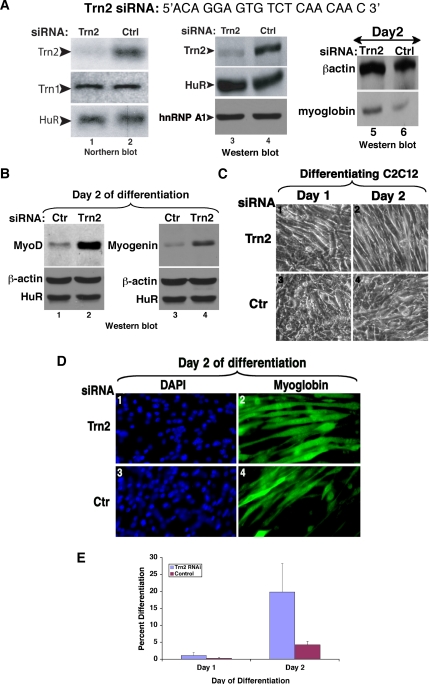
Figure 3.
Knockdown of Transportin 2 leads to enhanced myogenesis (A) The TRN2 siRNA duplex (Dharmacon) targets the TRN2 mRNA near the 5′ end of the message. A nonspecific control oligonucleotide was used as a negative control. Northern blot analysis was performed on 10 μg of total RNA isolated on day 0 of differentiation [48 h after transfection of siRNA duplexes (lanes 1–2)]. The membrane was probed with specific 32P-radiolabeled probes against TRN2, TRN1, and HuR (lanes 1 and 2). Western blot analysis was performed on 15 μg of total cell extract at the same time point (lanes 3 and 4) or at day 2 of differentiation (lanes 5 and 6). The membrane was probed with antibodies to TRN2, HuR, hnRNP A1 (lanes 3 and 4) or to myoglobin and β-actin (lanes 5 and 6) to determine the degree of differentiation after the siRNA treatments. (B) Total cell extracts from TRN2 siRNA- and control (ctr)-treated C2C12 cells were prepared on day 2 of differentiation. Western blotting using antibodies to MyoD (lanes 1 and 2) and myogenin (lanes 3 and 4) demonstrated increased expression of these MRFs in the absence of TRN2 compared with the control. (C) C2C12 myoblasts were transfected with TRN2 or Ctrl siRNA oligonucleotides, and differentiation was induced when cells reached 100% confluency. Phase-contrast pictures of a single representative field of view for each cell treatment on day 1 and day 2 of differentiation are shown. (D and E) TRN2 siRNA-treated and control cells were fixed, and immunofluorescence staining against myoglobin and DAPI was performed on C2C12 cells on day 2 of differentiation. (D) A single representative field of view for each cell treatment is shown. (E) The fusion index is shown and was calculated as described (Figure 1). Error bars, SD of three independent experiments.