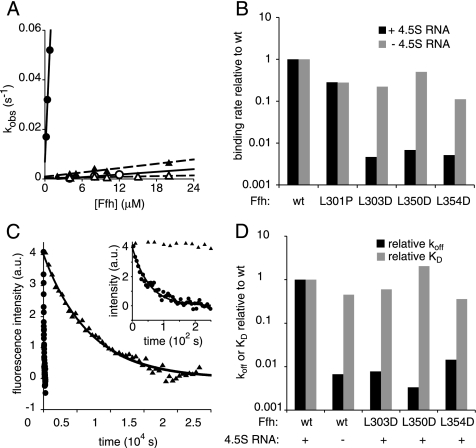
Figure 3.
Ffh mutations of L303D, L350D, and L354D abrogate the activity of the 4.5S RNA to catalyze association of Ffh and FtsY. (A) Observed rate constants for binding of wild-type Ffh (•, ○) or Ffh(L303D) (▴, ▵) in the presence (filled symbols) or absence (open symbols) of 4.5S RNA are plotted as a function of Ffh concentration. Lines represent fits to the equation kobs = kon ∗ [Ffh] + koff [solid lines for wt Ffh, dashed lines for Ffh(L303D)]. (B) The mutations selectively affect the binding rate in the presence but not absence of the 4.5S RNA. The binding rates relative to wt Ffh are plotted (note log-scaled Y axis). (C) Dissociation of wild-type (•) or Ffh(L303D) (▴) from FtsY was measured in the presence of the 4.5S RNA by adding GDP to trap dissociated complexes and monitored by changes in tryptophan fluorescence. Samples were excited at 290 nm, and fluorescence emission at 340 nm was recorded. The x-axis in the inset is expanded to show the curve for wild-type Ffh. Data were fit to a single exponential equation to calculate the koff. (D) Plot of the koff or KD of Ffh mutants relative to wild-type Ffh in the presence of the 4.5S RNA. kon, koff, and KD values are summarized in Table 2.