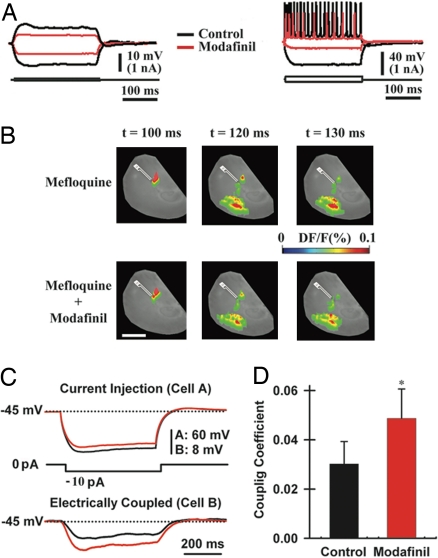
Fig. 3.
Modafinil increases electrotonic coupling among cortical interneurons. (A) Intracellular recordings from a pyramidal cell (Left) and an interneuron (Right) before (black) and after 50 μM modafinil (red). (B) VSDI responses after 50-min preincubation with mefloquine (50 μM, Upper) and 20 min after micropressure application of 50 μM modafinil to the cortex in the presence of mefloquine (Lower). (Scale bar, 1 mm.) (C) Dual-patch recording from a pair of cortical interneurons (in the presence of 2 μM tetrodotoxin) after the injection of a hyperpolarizing pulse into one neuron (cell A, Left) while recording the voltage deflection of the electrically coupled neuron (cell B, Right). (D) Mean coupling coefficients before (black bar; 0.030 ± 0.009) and after modafinil application (100 μM, red bar; 0.049 ± 0.012; n = 6 pairs). *, P = 0.02.