Fig. 1.
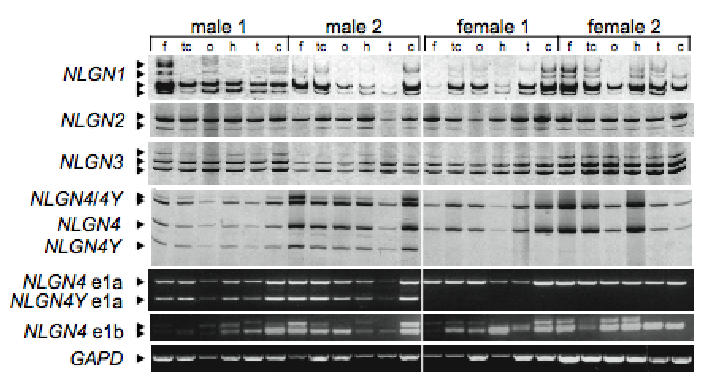
Expression of NLGNs in the human brain. Specific RT-PCRs were performed on total RNA from different brain regions using primers in exon 2 and 5 in order to analyse the different alternative spliced transcripts. To distinguish between NLGN4 and NLGN4Y mRNA, RT–PCRs were digested by NcoI. Using specific forward primers in exon 1a or exon 1b and reverse primers in exon 2, two alternative NLGN4 promoters were identified substituting the first exon 1a for 1b. Size of NLGN4 and NLGN4Y PCR differs by 193 bp. Exon 1b is specific to NLGN4 and contains an internal alternative donor splice site. The ages of the two males and the two females studied were 74, 42, 55, and 36 years old with a post-mortem delay of 10, 21, 24, and 2 h, respectively. f: frontal cortex, tc: temporal cortex, o: occipital cortex, h: hippocampus, t: thalamus; c: cerebellum. Normal control human brains were obtained at autopsy under guidelines approved by the ethics committee. DNA amplification and RT-PCRs were performed as described17. Alignment and sequences of all NLGN proteins and isoforms are available from the authors.
