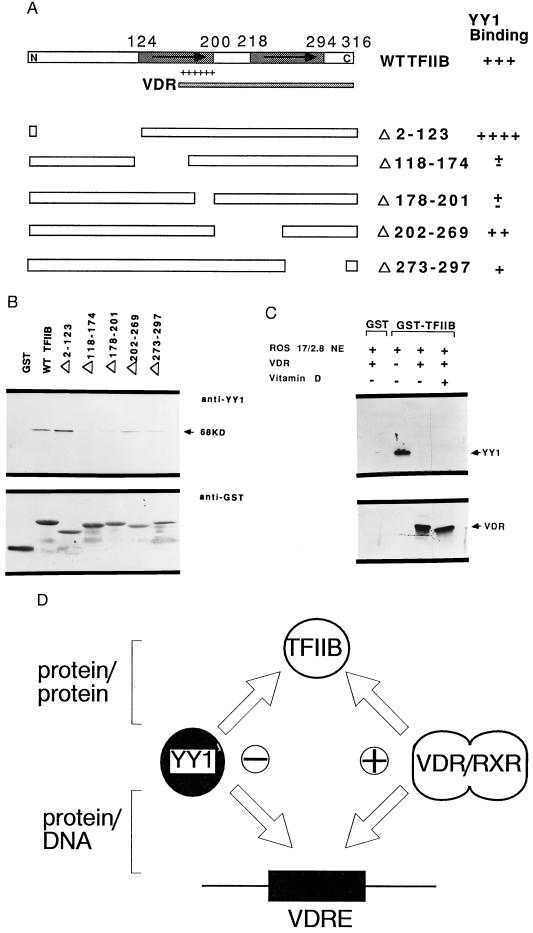
Figure 6.
YY1 binds to the basic region of TFIIB and competes for the VDR/RXR interaction with TFIIB. (A) Schematic representation of the TFIIB protein and a panel of wild-type and truncated GST-TFIIB fusion proteins. Indicated in the TFIIB diagram are the TFIIB repeat regions (arrows) and basic domain (+). The ability of truncated TFIIB proteins to interact with YY1 is shown in the right column. The TFIIB domains required for the interaction with VDR (cross-hatched bars) is indicated below the diagram of the wild-type protein. (B) Protein binding assay using a panel of GST-TFIIB fusion proteins linked to glutathione-Sepharose beads that were incubated with purified his-YY1. The YY1 signal, which is observed after Western blotting of protein bound to the beads, is indicated by the arrow. (C) YY1 and VDR compete for binding to TFIIB. ROS 17/2.8 nuclear extracts were incubated at 4°C with matrices containing GST or GST-TFIIB in the absence or presence of VDR (1 μg) with or without addition of 10−8 M vitamin D. (D) A model illustrating the mechanism by which YY1 may influence vitamin D dependent enhancement of OC transcription. This model suggests that YY1 exerts its inhibitory effect by interfering with the binding of VDR/RXR to VDRE, as well as by interfering with the interaction between DNA bound VDR/RXR and TFIIB.