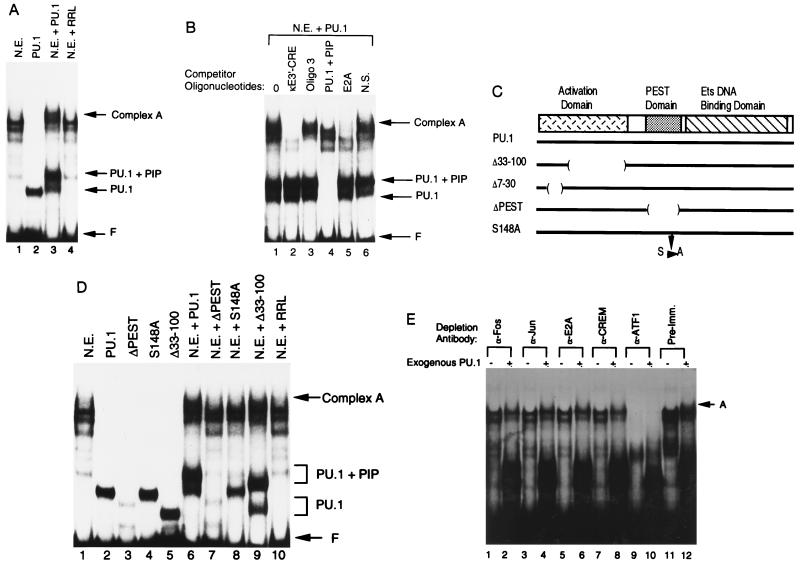
Figure 2.
Formation of a higher-order complex over the enhancer core. (A) EMSA was performed with the 3′-enhancer core sequence (residues 391–523) as a probe. Assays were performed with either S194 plasmacytoma nuclear extract (N.E.), PU.1 prepared by in vitro transcription and translation (PU.1), nuclear extract plus PU.1 (N.E. plus PU.1), or nuclear extract incubated with unprogrammed rabbit reticulocyte lysate (N.E. plus RRL). The positions of free probe (F), PU.1–DNA complex (PU.1), PU.1 plus PIP–DNA complex (PU.1 plus PIP), and complex A are indicated by the arrows at the right. (B) Complex A contains multiple enhancer binding proteins. EMSA was performed with the enhancer core probe and S194 nuclear extract plus exogenous PU.1. The various unlabeled competitor oligonucleotides added to the reactions are listed above each lane. The positions of various protein–DNA complexes are indicated by the arrows at the right. (C) Diagram of the PU.1 protein. The PU.1 transcriptional activation, PEST, and Ets DNA binding domains are indicated. Various PU.1 mutants used in this study are diagrammed below. (D) Complex A contains PIP. EMSA was performed with the enhancer core probe in the presence of various recombinant proteins alone or with S194 nuclear extract. Proteins included in each reaction are indicated above the lanes. (E) Identification of other proteins in complex A. EMSA was performed with the enhancer core probe and immunodepleted S194 nuclear extract. Antibodies used for immunodepletion are indicated above each lane. The presence or absence of exogenous PU.1 is indicated by a + or −, respectively.