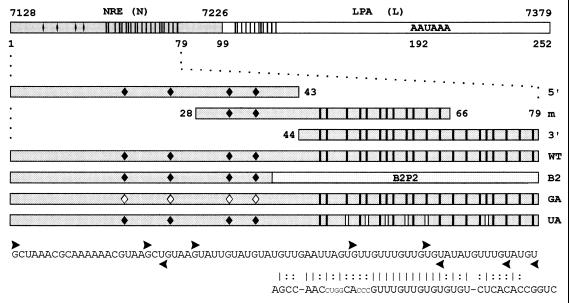
Figure 2.
Templates used to generate radiolabeled riboprobes and unlabeled competitor RNAs. Probe N: 79-nt minimal NRE and 20 nt downstream (HPV-16 nt 7128–7226). Probe L: 153-nt region (nt 7227–7379) containing the HPV-16 late poly(A) site (LPA). Probe 5′: 5′ portion of the 79-nt NRE containing four 5′ splice site homologies (♦). | = uridines present in the 3′ portion of probe N and within the putative weak binding site in L. Probe m: middle NRE section containing two 5′ splice site homologies and half of the G+U-rich element. Probe 3′: 3′ NRE portion containing a G+U-rich region with homology to a B2P2 binding site. Probe WT: 79-nt wild-type NRE. Probe B2: G+U-rich region substituted by the U2AF65 binding site B2P2 from the α-tropomyosin gene. Probe GA: HPV-16 NRE with G to A mutations in the putative first intron base of all four 5′ splice site homologies ♦. Probe UA: six U to A mutations in the G+U-rich region (| |). Vertical bars in the L fragment indicate partial homology to the G+U-rich element. ▸, first nucleotides retained in the 5′ deletion clones; ◂, last nucleotides retained in the 3′ deletion clones. The B2P2 sequence is shown; vertical bars indicate nucleotide homologies, and colons refer to conserved purine/pyrimidine patterns.